The kinetics of two-dimensional TCR and pMHC interactions determine T-cell responsiveness
- PMID: 20357766
- PMCID: PMC2925443
- DOI: 10.1038/nature08944
The kinetics of two-dimensional TCR and pMHC interactions determine T-cell responsiveness
Abstract
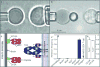
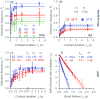
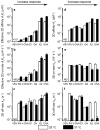
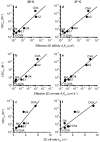
The T-cell receptor (TCR) interacts with peptide-major histocompatibility complexes (pMHC) to discriminate pathogens from self-antigens and trigger adaptive immune responses. Direct physical contact is required between the T cell and the antigen-presenting cell for cross-junctional binding where the TCR and pMHC are anchored on two-dimensional (2D) membranes of the apposing cells. Despite their 2D nature, TCR-pMHC binding kinetics have only been analysed three-dimensionally (3D) with a varying degree of correlation with the T-cell responsiveness. Here we use two mechanical assays to show high 2D affinities between a TCR and its antigenic pMHC driven by rapid on-rates. Compared to their 3D counterparts, 2D affinities and on-rates of the TCR for a panel of pMHC ligands possess far broader dynamic ranges that match that of their corresponding T-cell responses. The best 3D predictor of response is the off-rate, with agonist pMHC dissociating the slowest. In contrast, 2D off-rates are up to 8,300-fold faster, with the agonist pMHC dissociating the fastest. Our 2D data suggest rapid antigen sampling by T cells and serial engagement of a few agonist pMHCs by TCRs in a large self pMHC background. Thus, the cellular environment amplifies the intrinsic TCR-pMHC binding to generate broad affinities and rapid kinetics that determine T-cell responsiveness.
Figures
References
-
- Dustin ML, Bromley SK, Davis MM, Zhu C. Identification of self through two-dimensional chemistry and synapses. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol. 2001;17:133–157. - PubMed
-
- Davis MM, et al. Ligand recognition by alpha beta T cell receptors. Annu Rev Immunol. 1998;16:523–544. - PubMed
-
- Gascoigne NR, Zal T, Alam SM. T-cell receptor binding kinetics in T-cell development and activation. Expert Rev Mol Med 2001. 2001:1–17. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

