Carbon Dots as Nontoxic and High-Performance Fluorescence Imaging Agents
- PMID: 20357893
- PMCID: PMC2846368
- DOI: 10.1021/jp9085969
Carbon Dots as Nontoxic and High-Performance Fluorescence Imaging Agents
Abstract
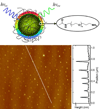
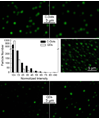
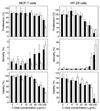
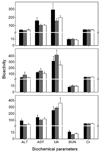
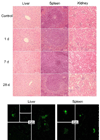
Fluorescent carbon dots (small carbon nanoparticles with the surface passivated by oligomeric PEG molecules) were evaluated for their cytotoxicity and in vivo toxicity and also for their optical imaging performance in reference to that of the commercially supplied CdSe/ZnS quantum dots. The results suggested that the carbon dots were biocompatible, and their performance as fluorescence imaging agents was competitive. The implication to the use of carbon dots for in vitro and in vivo applications is discussed.
Figures
References
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
