Botulinum toxin type A in post-stroke lower limb spasticity: a multicenter, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial
- PMID: 20358216
- PMCID: PMC2910313
- DOI: 10.1007/s00415-010-5526-3
Botulinum toxin type A in post-stroke lower limb spasticity: a multicenter, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial
Erratum in
- J Neurol. 2010 Aug;257(8):1416
Abstract
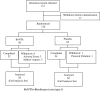
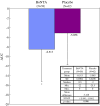
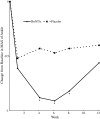
Lower limb spasticity in post-stroke patients can impair ambulation and reduces activities of daily living (ADL) performance of patients. Botulinum toxin type A (BoNTA) has been shown effective for upper limb spasticity. This study assesses the treatment of lower limb spasticity in a large placebo-controlled clinical trial. In this multicenter, randomized, double-blind, parallel-group, placebo-controlled study, we evaluate the efficacy and safety of one-time injections of botulinum toxin type A (BoNTA) in Japanese patients with post-stroke lower limb spasticity. One hundred twenty patients with lower limb spasticity were randomized to a single treatment with BoNTA 300 U or placebo. The tone of the ankle flexor was assessed at baseline and through 12 weeks using the Modified Ashworth Scale (MAS). Gait pattern and speed of gait were also assessed. The primary endpoint was area under the curve (AUC) of the change from baseline in the MAS ankle score. Significant improvement in spasticity with BoNTA 300 U was demonstrated by a mean difference in the AUC of the change from baseline in the MAS ankle score between the BoNTA and placebo groups (-3.428; 95% CIs, -5.841 to -1.016; p = 0.006; t test). A significantly greater decrease from baseline in the MAS ankle score was noted at weeks 4, 6 and 8 in the BoNTA group compared to the placebo group (p < 0.001). Significant improvement in the Clinicians Global Impression was noted by the investigator at weeks 4, 6 and 8 (p = 0.016-0.048, Wilcoxon test), but not by the patient or physical/occupational therapist. Assessments of gait pattern using the Physician's Rating Scale and speed of gait revealed no significant treatment differences but showed a tendency towards improvement with BoNTA. No marked difference was noted in the frequency of treatment-related adverse events between BoNTA and placebo groups. This was the first large-scale trial to indicate that BoNTA significantly reduced spasticity in lower limb muscles.
Trial registration: ClinicalTrials.gov NCT00460655.
Figures
References
-
- Lance JW. Symposium synopsis. In: Feldman RG, Young RR, Koella WP, editors. Spasticity: disordered motor control. Chicago: Year Book Medical Publishers; 1980. pp. 485–494.
-
- Grazko MA, Polo KB, Jabbari B. Botulinum toxin A for spasticity, muscle spasms and rigidity. Neurology. 1995;45:712–717. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

