Kinetic and inhibition studies of dihydroxybenzoate-AMP ligase from Escherichia coli
- PMID: 20359185
- PMCID: PMC2860672
- DOI: 10.1021/bi100350c
Kinetic and inhibition studies of dihydroxybenzoate-AMP ligase from Escherichia coli
Abstract
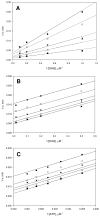
Inhibition of siderophore biosynthetic pathways in pathogenic bacteria represents a promising strategy for antibacterial drug development. Escherichia coli synthesize and secrete the small molecule iron chelator siderophore, enterobactin, in response to intracellular iron depletion. Here we describe a detailed kinetic analysis of EntE, one of six enzymes in the enterobactin synthetase gene cluster. EntE catalyzes the ATP-dependent condensation of 2,3-dihydroxybenzoic acid (DHB) and phosphopantetheinylated EntB (holo-EntB) to form covalently arylated EntB, a product that is vital for the final assembly of enterobactin. Initial velocity studies show that EntE proceeds via a bi-uni-uni-bi ping-pong kinetic mechanism with a k(cat) equal to 2.8 s(-1) and K(m) values of 2.5, 430, and 2.9 microM for DHB, ATP, and holo-EntB-ArCP, respectively. Inhibition and direct binding experiments suggest that, during the first half-reaction (adenylation), DHB binds first to the free enzyme, followed by ATP and the release of pyrophosphate to form the adenylate intermediate. During the second half-reaction (ligation), phosphopantetheinylated EntB binds to the enzyme followed by the release of products, AMP and arylated EntB. Two hydrolytically stable adenylate analogues, 5'-O-[N-(salicyl)sulfamoyl]adenosine (Sal-AMS) and 5'-O-[N-(2,3-dihydroxybenzoyl)sulfamoyl]adenosine (DHB-AMS), are shown to act as slow-onset tight-binding inhibitors of the enzyme with (app)K(i) values of 0.9 and 3.8 nM, respectively. Direct binding experiments, via isothermal titration calorimetry, reveal low picomolar dissociation constants for both analogues with respect to EntE. The tight binding of Sal-AMS and DHB-AMS to EntE suggests that these compounds may be developed further as effective antibiotics targeted to this enzyme.
Figures



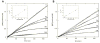


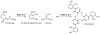



Similar articles
-
Ligand-induced conformational rearrangements promote interaction between the Escherichia coli enterobactin biosynthetic proteins EntE and EntB.J Mol Biol. 2009 Oct 30;393(3):658-71. doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2009.08.036. Epub 2009 Aug 20. J Mol Biol. 2009. PMID: 19699210
-
Enterobactin biosynthesis in Escherichia coli: isochorismate lyase (EntB) is a bifunctional enzyme that is phosphopantetheinylated by EntD and then acylated by EntE using ATP and 2,3-dihydroxybenzoate.Biochemistry. 1997 Jul 15;36(28):8495-503. doi: 10.1021/bi970453p. Biochemistry. 1997. PMID: 9214294
-
The enterobactin biosynthetic intermediate 2,3-dihydroxybenzoic acid is a competitive inhibitor of the Escherichia coli isochorismatase EntB.Protein Sci. 2025 Jun;34(6):e70160. doi: 10.1002/pro.70160. Protein Sci. 2025. PMID: 40400396 Free PMC article.
-
Reconstitution and characterization of the Escherichia coli enterobactin synthetase from EntB, EntE, and EntF.Biochemistry. 1998 Feb 24;37(8):2648-59. doi: 10.1021/bi9726584. Biochemistry. 1998. PMID: 9485415
-
Enzymatic adenylation of 2,3-dihydroxybenzoate is enhanced by a protein-protein interaction between Escherichia coli 2,3-dihydro-2,3-dihydroxybenzoate dehydrogenase (EntA) and 2,3-dihydroxybenzoate-AMP ligase (EntE).Biochemistry. 2011 Feb 1;50(4):533-45. doi: 10.1021/bi101558v. Epub 2010 Dec 31. Biochemistry. 2011. PMID: 21166461
Cited by
-
Kinetic Analyses of the Siderophore Biosynthesis Inhibitor Salicyl-AMS and Analogues as MbtA Inhibitors and Antimycobacterial Agents.Biochemistry. 2019 Feb 12;58(6):833-847. doi: 10.1021/acs.biochem.8b01153. Epub 2019 Jan 10. Biochemistry. 2019. PMID: 30582694 Free PMC article.
-
Expanding the results of a high throughput screen against an isochorismate-pyruvate lyase to enzymes of a similar scaffold or mechanism.Bioorg Med Chem. 2014 Nov 1;22(21):5961-9. doi: 10.1016/j.bmc.2014.09.010. Epub 2014 Sep 16. Bioorg Med Chem. 2014. PMID: 25282647 Free PMC article.
-
Stable analogues of OSB-AMP: potent inhibitors of MenE, the o-succinylbenzoate-CoA synthetase from bacterial menaquinone biosynthesis.Chembiochem. 2012 Jan 2;13(1):129-36. doi: 10.1002/cbic.201100585. Epub 2011 Nov 23. Chembiochem. 2012. PMID: 22109989 Free PMC article.
-
Biosynthesis, Mechanism of Action, and Inhibition of the Enterotoxin Tilimycin Produced by the Opportunistic Pathogen Klebsiella oxytoca.ACS Infect Dis. 2020 Jul 10;6(7):1976-1997. doi: 10.1021/acsinfecdis.0c00326. Epub 2020 Jun 24. ACS Infect Dis. 2020. PMID: 32485104 Free PMC article.
-
Cardiovascular biomarkers predict susceptibility to lung injury in World Trade Center dust-exposed firefighters.Eur Respir J. 2013 May;41(5):1023-30. doi: 10.1183/09031936.00077012. Epub 2012 Aug 16. Eur Respir J. 2013. PMID: 22903969 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Gehring AM, Bradley KA, Walsh CT. Enterobactin biosynthesis in Escherichia coli: isochorismate lyase (EntB) is a bifunctional enzyme that is phosphopantetheinylated by EntD and then acylated by EntE using ATP and 2,3-dihydroxybenzoate. Biochemistry. 1997;36:8495–8503. - PubMed
-
- Gehring AM, Mori I, Walsh CT. Reconstitution and characterization of the Escherichia coli enterobactin synthetase from EntB, EntE, and EntF. Biochemistry. 1998;37:2648–2659. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

