Antibody validation
- PMID: 20359301
- PMCID: PMC3891910
- DOI: 10.2144/000113382
Antibody validation
Erratum in
- Biotechniques. 2010 May;48(5):351
Abstract
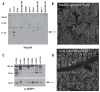
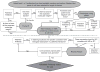
Antibodies are among the most frequently used tools in basic science research and in clinical assays, but there are no universally accepted guidelines or standardized methods for determining the validity of these reagents. Furthermore, for commercially available antibodies, it is clear that what is on the label does not necessarily correspond to what is in the tube. To validate an antibody, it must be shown to be specific, selective, and reproducible in the context for which it is to be used. In this review, we highlight the common pitfalls when working with antibodies, common practices for validating antibodies, and levels of commercial antibody validation for seven vendors. Finally, we share our algorithm for antibody validation for immunohistochemistry and quantitative immunofluorescence.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures




References
-
- Dowsett M, Hanna WM, Kockx M, Penault-Llorca F, Rüschoff J, Gutjahr T, Habben K, van de Vijver MJ. Standardization of HER2 testing: results of an international proficiency-testing ring study. Mod Pathol. 2007;20:584–591. - PubMed
-
- Goldstein NS, Hewitt SM, Taylor CR, Yaziji H, Hicks DG and Members of the Ad-Hoc Committee on Immunohistochemistry Standardization. Recommendations for improved standardization of immunohistochemistry. Appl Immunohistochem Mol Morphol. 2007;15:124–133. - PubMed
-
- Shi S-R, Liu C, Taylor CR. Standardization of immunohistochemistry for formalin-fixed, paraffin-embedded tissue sections based on the antigen-retrieval technique: from experiments to hypothesis. J Histochem Cytochem. 2007;55:105–109. - PubMed
-
- Wolff AC, Hammond MEH, Schwartz JN, Hagerty KL, Allred DC, Cote RJ, Dowsett M, Fitzgibbons PL, et al. American Society of Clinical Oncology/College of American Pathologists guideline recommendations for human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 testing in breast cancer. J Clin Oncol. 2007;25:118–145. - PubMed
-
- Hicks DG, Kulkarni S. HER2+ breast cancer: review of biologic relevance and optimal use of diagnostic tools. Am J Clin Pathol. 2008;129:263–273. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
