Zoonotic hepatitis E: animal reservoirs and emerging risks
- PMID: 20359452
- PMCID: PMC2865210
- DOI: 10.1051/vetres/2010018
Zoonotic hepatitis E: animal reservoirs and emerging risks
Abstract
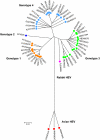
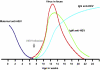
Hepatitis E virus (HEV) is responsible for enterically-transmitted acute hepatitis in humans with two distinct epidemiological patterns. In endemic regions, large waterborne epidemics with thousands of people affected have been observed, and, in contrast, in non-endemic regions, sporadic cases have been described. Although contaminated water has been well documented as the source of infection in endemic regions, the modes of transmission in non-endemic regions are much less known. HEV is a single-strand, positive-sense RNA virus which is classified in the Hepeviridae family with at least four known main genotypes (1-4) of mammalian HEV and one avian HEV. HEV is unique among the known hepatitis viruses, in which it has an animal reservoir. In contrast to humans, swine and other mammalian animal species infected by HEV generally remain asymptomatic, whereas chickens infected by avian HEV may develop a disease known as Hepatitis-Splenomegaly syndrome. HEV genotypes 1 and 2 are found exclusively in humans while genotypes 3 and 4 are found both in humans and other mammals. Several lines of evidence indicate that, in some cases involving HEV genotypes 3 and 4, animal to human transmissions occur. Furthermore, individuals with direct contact with animals are at higher risk of HEV infection. Cross-species infections with HEV genotypes 3 and 4 have been demonstrated experimentally. However, not all sources of human infections have been identified thus far and in many cases, the origin of HEV infection in humans remains unknown.
© INRA, EDP Sciences, 2010.
Figures
References
-
- Aggarwal R., Naik S.R., Hepatitis E: intrafamilial transmission versus waterborne spread, J. Hepatol. (1994) 21:718–723 - PubMed
-
- Aggarwal R., Kini D., Sofat S., Naik S.R., Krawczynski K., Duration of viraemia and faecal viral excretion in acute hepatitis E, Lancet (2000) 356:1081–1082 - PubMed
-
- Aggarwal R., Kamili S., Spelbring J., Krawczynski K., Experimental studies on subclinical hepatitis E virus infection in cynomolgus macaques, J. Infect. Dis. (2001) 184:1380–1385 - PubMed
-
- Agrawal S., Gupta D., Panda S.K., The 3′ end of hepatitis E virus (HEV) genome binds specifically to the viral RNA-dependent RNA polymerase (RdRp), Virology (2001) 282:87–101 - PubMed
-
- Andersson M.I., Hughes J., Gordon F.H., Ijaz S., Donati M., Of pigs and pregnancy, Lancet (2008) 372:1192. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
