Structure of the FoxM1 DNA-recognition domain bound to a promoter sequence
- PMID: 20360045
- PMCID: PMC2910063
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkq194
Structure of the FoxM1 DNA-recognition domain bound to a promoter sequence
Abstract
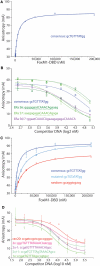
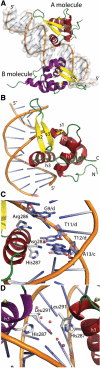
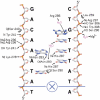
FoxM1 is a member of the Forkhead family of transcription factors and is implicated in inducing cell proliferation and some forms of tumorigenesis. It binds promoter regions with a preference for tandem repeats of a consensus 'TAAACA' recognition sequence. The affinity of the isolated FoxM1 DNA-binding domain for this site is in the micromolar range, lower than observed for other Forkhead proteins. To explain these FoxM1 features, we determined the crystal structure of its DNA-binding domain in complex with a tandem recognition sequence. FoxM1 adopts the winged-helix fold, typical of the Forkhead family. Neither 'wing' of the fold however, makes significant contacts with the DNA, while the second, C-terminal, wing adopts an unusual ordered conformation across the back of the molecule. The lack of standard DNA-'wing' interactions may be a reason for FoxM1's relatively low affinity. The role of the 'wings' is possibly undertaken by other FoxM1 regions outside the DBD, that could interact with the target DNA directly or mediate interactions with other binding partners. Finally, we were unable to show a clear preference for tandem consensus site recognition in DNA-binding, transcription activation or bioinformatics analysis; FoxM1's moniker, 'Trident', is not supported by our data.
Figures
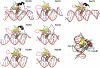
Similar articles
-
FOXM1 binds directly to non-consensus sequences in the human genome.Genome Biol. 2015 Jun 23;16(1):130. doi: 10.1186/s13059-015-0696-z. Genome Biol. 2015. PMID: 26100407 Free PMC article.
-
Crystal structure of the human FOXK1a-DNA complex and its implications on the diverse binding specificity of winged helix/forkhead proteins.J Biol Chem. 2006 Jun 23;281(25):17400-17409. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M600478200. Epub 2006 Apr 18. J Biol Chem. 2006. PMID: 16624804
-
Mechanistic Insights into the Preference for Tandem Binding Sites in DNA Recognition by FOXM1.J Mol Biol. 2022 Mar 15;434(5):167426. doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2021.167426. Epub 2021 Dec 29. J Mol Biol. 2022. PMID: 34973238
-
The transcription factor FOXM1 (Forkhead box M1): proliferation-specific expression, transcription factor function, target genes, mouse models, and normal biological roles.Adv Cancer Res. 2013;118:97-398. doi: 10.1016/B978-0-12-407173-5.00004-2. Adv Cancer Res. 2013. PMID: 23768511 Review.
-
Multiple modes of chromatin remodeling by Forkhead box proteins.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2012 Jul;1819(7):707-15. doi: 10.1016/j.bbagrm.2012.02.018. Epub 2012 Mar 2. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2012. PMID: 22406422 Review.
Cited by
-
DNA-binding specificity changes in the evolution of forkhead transcription factors.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2013 Jul 23;110(30):12349-54. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1310430110. Epub 2013 Jul 8. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2013. PMID: 23836653 Free PMC article.
-
ErbB2, FoxM1 and 14-3-3ζ prime breast cancer cells for invasion in response to ionizing radiation.Oncogene. 2014 Jan 30;33(5):589-98. doi: 10.1038/onc.2012.629. Epub 2013 Jan 14. Oncogene. 2014. PMID: 23318431 Free PMC article.
-
Crystal structure of the N-terminal region of human Ash2L shows a winged-helix motif involved in DNA binding.EMBO Rep. 2011 Jun 10;12(8):797-803. doi: 10.1038/embor.2011.101. EMBO Rep. 2011. PMID: 21660059 Free PMC article.
-
The development of an anti-cancer peptide M1-21 targeting transcription factor FOXM1.Cell Biosci. 2023 Jun 21;13(1):114. doi: 10.1186/s13578-023-01059-7. Cell Biosci. 2023. PMID: 37344857 Free PMC article.
-
Timing of transcription during the cell cycle: Protein complexes binding to E2F, E2F/CLE, CDE/CHR, or CHR promoter elements define early and late cell cycle gene expression.Oncotarget. 2016 Jul 28;8(58):97736-97748. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.10888. eCollection 2017 Nov 17. Oncotarget. 2016. PMID: 29228647 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Wierstra I, Alves J. The central domain of transcription factor FOXM1c directly interacts with itself in vivo and switches from an essential to an inhibitory domain depending on the FOXM1c binding site. Biol. Chem. 2007;388:805–818. - PubMed
-
- Liu M, Dai B, Kang SH, Ban K, Huang FJ, Lang FF, Aldape KD, Xie TX, Pelloski CE, Xie K, et al. FoxM1B is overexpressed in human glioblastomas and critically regulates the tumorigenicity of glioma cells. Cancer Res. 2006;66:3593–3602. - PubMed
-
- van den Boom J, Wolter M, Kuick R, Misek DE, Youkilis AS, Wechsler DS, Sommer C, Reifenberger G, Hanash SM. Characterization of gene expression profiles associated with glioma progression using oligonucleotide-based microarray analysis and real-time reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction. Am. J. Pathol. 2003;163:1033–1043. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

