Non-canonical DNA transcription enzymes and the conservation of two-barrel RNA polymerases
- PMID: 20360047
- PMCID: PMC2919709
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkq201
Non-canonical DNA transcription enzymes and the conservation of two-barrel RNA polymerases
Abstract
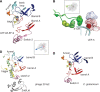
DNA transcription depends on multimeric RNA polymerases that are exceptionally conserved in all cellular organisms, with an active site region of >500 amino acids mainly harboured by their Rpb1 and Rpb2 subunits. Together with the distantly related eukaryotic RNA-dependent polymerases involved in gene silencing, they form a monophyletic family of ribonucleotide polymerases with a similarly organized active site region based on two double-Psi barrels. Recent viral and phage genome sequencing have added a surprising variety of putative nucleotide polymerases to this protein family. These proteins have highly divergent subunit composition and amino acid sequences, but always contain eight invariant amino acids forming a universally conserved catalytic site shared by all members of the two-barrel protein family. Moreover, the highly conserved 'funnel' and 'switch 2' components of the active site region are shared by all putative DNA-dependent RNA polymerases and may thus determine their capacity to transcribe double-stranded DNA templates.
Figures



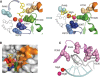
Similar articles
-
Multisubunit RNA Polymerases of Jumbo Bacteriophages.Viruses. 2020 Sep 23;12(10):1064. doi: 10.3390/v12101064. Viruses. 2020. PMID: 32977622 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Evolutionary connection between the catalytic subunits of DNA-dependent RNA polymerases and eukaryotic RNA-dependent RNA polymerases and the origin of RNA polymerases.BMC Struct Biol. 2003 Jan 28;3:1. doi: 10.1186/1472-6807-3-1. Epub 2003 Jan 28. BMC Struct Biol. 2003. PMID: 12553882 Free PMC article.
-
The Extended "Two-Barrel" Polymerases Superfamily: Structure, Function and Evolution.J Mol Biol. 2019 Sep 20;431(20):4167-4183. doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2019.05.017. Epub 2019 May 17. J Mol Biol. 2019. PMID: 31103775 Review.
-
Evolution of viral DNA-dependent RNA polymerases.Virus Genes. 1995;11(2-3):271-84. doi: 10.1007/BF01728665. Virus Genes. 1995. PMID: 8828152 Review.
-
Functional organization of the Rpb5 subunit shared by the three yeast RNA polymerases.Nucleic Acids Res. 2007;35(2):634-47. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkl686. Epub 2006 Dec 19. Nucleic Acids Res. 2007. PMID: 17179178 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Single-peptide DNA-dependent RNA polymerase homologous to multi-subunit RNA polymerase.Nat Commun. 2017 Jun 6;8:15774. doi: 10.1038/ncomms15774. Nat Commun. 2017. PMID: 28585540 Free PMC article.
-
Multisubunit RNA Polymerases of Jumbo Bacteriophages.Viruses. 2020 Sep 23;12(10):1064. doi: 10.3390/v12101064. Viruses. 2020. PMID: 32977622 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A non-canonical multisubunit RNA polymerase encoded by the AR9 phage recognizes the template strand of its uracil-containing promoters.Nucleic Acids Res. 2017 Jun 2;45(10):5958-5967. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkx264. Nucleic Acids Res. 2017. PMID: 28402520 Free PMC article.
-
Gene flow and biological conflict systems in the origin and evolution of eukaryotes.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2012 Jun 29;2:89. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2012.00089. eCollection 2012. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2012. PMID: 22919680 Free PMC article.
-
Discovery of an expansive bacteriophage family that includes the most abundant viruses from the human gut.Nat Microbiol. 2018 Jan;3(1):38-46. doi: 10.1038/s41564-017-0053-y. Epub 2017 Nov 13. Nat Microbiol. 2018. PMID: 29133882 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Cermakian N, Ikeda TM, Miramontes P, Lang BF, Gray MW, Cedergren R. On the evolution of the single-subunit RNA polymerases. J. Mol. Evol. 1997;45:671–681. - PubMed
-
- Werner F, Weinzierl RO. A recombinant RNA polymerase II-like enzyme capable of promoter-specific transcription. Mol. Cell. 2002;10:635–646. - PubMed
-
- Zhang G, Campbell EA, Minakhin L, Richter C, Severinov K, Darst SA. Crystal structure of Thermus aquaticus core RNA polymerase at 3.3 A resolution. Cell. 1999;98:811–824. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

