Discontinuation of infliximab after attaining low disease activity in patients with rheumatoid arthritis: RRR (remission induction by Remicade in RA) study
- PMID: 20360136
- PMCID: PMC3015067
- DOI: 10.1136/ard.2009.121491
Discontinuation of infliximab after attaining low disease activity in patients with rheumatoid arthritis: RRR (remission induction by Remicade in RA) study
Abstract
Background: Tumour necrosis factor (TNF) inhibitors enable tight control of disease activity in patients with rheumatoid arthritis (RA). Discontinuation of TNF inhibitors after acquisition of low disease activity (LDA) is important for safety and economic reasons.
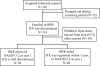
Objective: To determine whether infliximab might be discontinued after achievement of LDA in patients with RA and to evaluate progression of articular destruction during the discontinuation.
Methods: 114 patients with RA who had received infliximab treatment, and whose Disease Activity Score, including a 28-joint count (DAS28) was <3.2 (LDA) for 24 weeks, were studied.
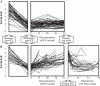
Results: The mean disease duration of the 114 patients was 5.9 years, mean DAS28 5.5 and mean modified total Sharp score (mTSS) 63.3. After maintaining LDA for >24 weeks by infliximab treatment, the drug was discontinued and DAS28 in 102 patients was evaluated at year 1. Fifty-six patients (55%) continued to have DAS28<3.2 and 43% reached DAS<2.6 at 1 year after discontinuing infliximab. For 46 patients remission induction by Remicade in RA (RRR) failed: disease in 29 patients flared within 1 year and DAS28 was >3.2 at year 1 in 17 patients. Yearly progression of mTSS (DeltaTSS) remained <0.5 in 67% and 44% of the RRR-achieved and RRR-failed groups, respectively. The estimated DeltamTSS was 0.3 and 1.6 and Health Assessment Questionnaire-Disability Index was 0.174 and 0.614 in the RRR-achieved and RRR-failed groups, respectively, 1 year after the discontinuation.
Conclusion: After attaining LDA by infliximab, 56 (55%) of the 102 patients with RA were able to discontinue infliximab for >1 year without progression of radiological articular destruction.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures


References
-
- Klareskog L, Catrina AI, Paget S. Rheumatoid arthritis. Lancet 2009;373:659–72 - PubMed
-
- Emery P, Breedveld FC, Hall S, et al. Comparison of methotrexate monotherapy with a combination of methotrexate and etanercept in active, early, moderate to severe rheumatoid arthritis (COMET): a randomised, double-blind, parallel treatment trial. Lancet 2008;372:375–82 - PubMed
-
- Breedveld FC, Weisman MH, Kavanaugh AF, et al. The PREMIER study: a multicenter, randomized, double-blind clinical trial of combination therapy with adalimumab plus methotrexate versus methotrexate alone or adalimumab alone in patients with early, aggressive rheumatoid arthritis who had not had previous methotrexate treatment. Arthritis Rheum 2006;54:26–37 - PubMed
-
- Klareskog L, van der Heijde D, de Jager JP, et al. Therapeutic effect of the combination of etanercept and methotrexate compared with each treatment alone in patients with rheumatoid arthritis: double-blind randomised controlled trial. Lancet 2004;363:675–81 - PubMed
-
- St Clair EW, van der Heijde DM, Smolen JS, et al. For the Active-Controlled Study of Patients Receiving Infliximab for the Treatment of Rheumatoid Arthritis of Early Onset Study Group. Combination of infliximab and methotrexate therapy for early rheumatoid arthritis: a randomized, controlled trial. Arthritis Rheum 2004;50:3432–43 - PubMed

