Comparative gene expression analysis of susceptible and resistant near-isogenic lines in common wheat infected by Puccinia triticina
- PMID: 20360266
- PMCID: PMC2920755
- DOI: 10.1093/dnares/dsq009
Comparative gene expression analysis of susceptible and resistant near-isogenic lines in common wheat infected by Puccinia triticina
Abstract
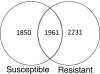
Gene expression after leaf rust infection was compared in near-isogenic wheat lines differing in the Lr10 leaf rust resistance gene. RNA from susceptible and resistant plants was used for cDNA library construction. In total, 55 008 ESTs were sequenced from the two libraries, then combined and assembled into 14 268 unigenes for further analysis. Of these ESTs, 89% encoded proteins similar to (E value of < or =10(-5)) characterized or annotated proteins from the NCBI non-redundant database representing diverse molecular functions, cellular localization and biological processes based on gene ontology classification. Further, the unigenes were classified into susceptible and resistant classes based on the EST members assembled from the respective libraries. Several genes from the resistant sample (14-3-3 protein, wali5 protein, actin-depolymerization factor and ADP-ribosylation factor) and the susceptible sample (brown plant hopper resistance protein, caffeic acid O-methyltransferase, pathogenesis-related protein and senescence-associated protein) were selected and their differential expression in the resistant and susceptible samples collected at different time points after leaf rust infection was confirmed by RT-PCR analysis. The molecular pathogenicity of leaf rust in wheat was studied and the EST data generated made a foundation for future studies.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Analysis of the wheat and Puccinia triticina (leaf rust) proteomes during a susceptible host-pathogen interaction.Proteomics. 2006 Mar;6(6):1897-907. doi: 10.1002/pmic.200500351. Proteomics. 2006. PMID: 16479535
-
Pathogen-regulated genes in wheat isogenic lines differing in resistance to brown rust Puccinia triticina.BMC Genomics. 2015 Oct 5;16:742. doi: 10.1186/s12864-015-1932-3. BMC Genomics. 2015. PMID: 26438375 Free PMC article.
-
Identification and molecular characterization of a trans-acting small interfering RNA producing locus regulating leaf rust responsive gene expression in wheat (Triticum aestivum L.).Planta. 2017 Nov;246(5):939-957. doi: 10.1007/s00425-017-2744-2. Epub 2017 Jul 14. Planta. 2017. PMID: 28710588
-
Wheat leaf rust caused by Puccinia triticina.Mol Plant Pathol. 2008 Sep;9(5):563-75. doi: 10.1111/j.1364-3703.2008.00487.x. Mol Plant Pathol. 2008. PMID: 19018988 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The progress of leaf rust research in wheat.Fungal Biol. 2020 Jun;124(6):537-550. doi: 10.1016/j.funbio.2020.02.013. Epub 2020 Feb 29. Fungal Biol. 2020. PMID: 32448445 Review.
Cited by
-
Comparative transcriptomics of stem rust resistance in wheat NILs mediated by Sr24 rust resistance gene.PLoS One. 2023 Dec 11;18(12):e0295202. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0295202. eCollection 2023. PLoS One. 2023. PMID: 38079439 Free PMC article.
-
Targeted spatio-temporal expression based characterization of state of infection and time-point of maximum defense in wheat NILs during leaf rust infection.Mol Biol Rep. 2012 Oct;39(10):9373-82. doi: 10.1007/s11033-012-1801-y. Epub 2012 Jun 27. Mol Biol Rep. 2012. PMID: 22736109
-
The Soybean Rhg1 locus for resistance to the soybean cyst nematode Heterodera glycines regulates the expression of a large number of stress- and defense-related genes in degenerating feeding cells.Plant Physiol. 2011 Apr;155(4):1960-75. doi: 10.1104/pp.110.167536. Epub 2011 Feb 18. Plant Physiol. 2011. PMID: 21335526 Free PMC article.
-
Expression of the maize ZmGF14-6 gene in rice confers tolerance to drought stress while enhancing susceptibility to pathogen infection.J Exp Bot. 2012 Jan;63(2):983-99. doi: 10.1093/jxb/err328. Epub 2011 Oct 20. J Exp Bot. 2012. PMID: 22016430 Free PMC article.
-
Comprehensive functional analyses of expressed sequence tags in common wheat (Triticum aestivum).DNA Res. 2012 Apr;19(2):165-77. doi: 10.1093/dnares/dss001. Epub 2012 Feb 14. DNA Res. 2012. PMID: 22334568 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Kolmer J.A. Tracking wheat rust on a continental scale. Curr. Opin. Plant Biol. 2005;8:441–9. doi:10.1016/j.pbi.2005.05.001. - DOI - PubMed
-
- McIntosh R.A., Dubcovsky J., Rogers J., Morris C., Appels R., Xia X.C. Catalogue of gene symbols for wheat-2009 supplement. KOMUGI Integrated Wheat Science Database. 2009 http://www.shigen.nig.ac.jp/wheat/komugi/genes/macgene .
-
- Cloutier S., McCallum B.D., Loutre C., et al. Leaf rust resistance gene Lr1, isolated from bread wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) is a member of the large psr567 gene family. Plant Mol. Biol. 2007;65:93–106. doi:10.1007/s11103-007-9201-8. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Feuillet C., Travella S., Stein N., Albar L., Nublat L., Keller B. Map-based isolation of the leaf rust disease resistance gene Lr10 from the hexaploid wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) genome. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA. 2003;100:15253–8. doi:10.1073/pnas.2435133100. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

