Screening and brief intervention for underage drinkers
- PMID: 20360296
- PMCID: PMC2848426
- DOI: 10.4065/mcp.2008.0638
Screening and brief intervention for underage drinkers
Abstract
In a 2007 report, the US Surgeon General called for health care professionals to renew efforts to reduce underage drinking. Focusing on the adolescent patient, this review provides health care professionals with recommendations for alcohol-related screening, brief intervention, and referral to treatment. MEDLINE and published reviews were used to identify relevant literature. Several brief screening methods have been shown to effectively identify underage drinkers likely to have alcohol use disorders. After diagnostic assessment when germane, the initial intervention typically focuses on education, motivation for change, and consideration of treatment options. Internet-accessible resources providing effective brief interventions are available, along with supplemental suggestions for parents. Recent changes in federal and commercial insurance reimbursement policies provide some fiscal support for these services, although rate increases and expanded applicability may be required to prompt the participation of many practitioners. Nevertheless, advances in clinical methods and progress on reimbursement policies have made screening and brief intervention for underage drinking more feasible in general health care practice.
Figures
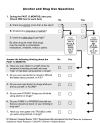
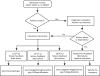
References
-
- Thatcher DL, Clark DB. Adolescent alcohol abuse and dependence: development, diagnosis, treatment, and outcomes. Curr Psychiatry Rev. 2006;2(1):159-177
-
- Clark DB. The natural history of adolescent alcohol use disorders. Addiction 2004;99(suppl 1):5-22 - PubMed
-
- Hingson RW, Heeren T, Winter MR. Age at drinking onset and alcohol dependence: age at onset, duration, and severity. Arch Pediatr Adolesc Med. 2006;160(7):739-746 - PubMed
-
- Grant BF, Dawson DA, Stinson FS, Chou SP, Dufour MC, Pickering RP. The 12-month prevalence and trends in DSM-IV alcohol abuse and dependence: United States, 1991-1992 and 2001-2002. Drug Alcohol Depend 2004;74(3):223-234 - PubMed
-
- Knight JR, Wechsler H, Kuo M, Seibring M, Weitzman ER, Schuckit MA. Alcohol abuse and dependence among U.S. college students. J Stud Alcohol. 2002;63(3):263-270 - PubMed

