Efficacy and safety of long-term fluoxetine versus lithium monotherapy of bipolar II disorder: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-substitution study
- PMID: 20360317
- PMCID: PMC2896440
- DOI: 10.1176/appi.ajp.2009.09020284
Efficacy and safety of long-term fluoxetine versus lithium monotherapy of bipolar II disorder: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-substitution study
Abstract
Objective: The authors examined the safety and efficacy of long-term fluoxetine monotherapy, lithium monotherapy, and placebo therapy in preventing relapse and recurrence of bipolar type II major depressive episode. The authors hypothesized that fluoxetine monotherapy would be superior to lithium monotherapy with a similar hypomanic mood conversion rate.
Method: Patients at least 18 years old who recovered from their major depressive episode during initial open-label fluoxetine monotherapy were randomly assigned to receive 50 weeks of double-blind monotherapy with fluoxetine at 10-40 mg/day, lithium at 300-1200 mg/day, or placebo. The primary outcome measure was time to relapse or recurrence. Secondary outcome measures included the proportion of patients remaining well and the frequency of hypomanic symptoms.
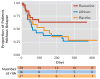
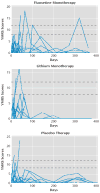
Results: There were no significant differences in clinical or demographic characteristics among the fluoxetine (N=28), lithium (N=26), and placebo (N=27) groups. The mean time to relapse was 249.9 days for the fluoxetine group, 156.4 days for the lithium group, and 186.9 days for the placebo group. The hazard of relapse was significantly lower with fluoxetine compared with lithium, and the estimated hazard of relapse with lithium was 2.5 times greater than with fluoxetine. There were no statistically significant or clinically meaningful differences in hypomanic symptoms among treatment groups over time. One patient taking fluoxetine and one patient taking placebo discontinued treatment because of hypomania.
Conclusions: These findings suggest that long-term fluoxetine monotherapy may provide superior relapse-prevention benefit relative to lithium monotherapy after recovery from bipolar II major depressive episode without an increase in hypomanic mood conversion episodes.
Trial registration: ClinicalTrials.gov NCT00044616.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors report no financial relationships with commercial interests.
Figures

Comment in
-
Is there a role for antidepressants in the treatment of bipolar II depression?Am J Psychiatry. 2010 Jul;167(7):738-40. doi: 10.1176/appi.ajp.2010.10040590. Am J Psychiatry. 2010. PMID: 20595424 No abstract available.
-
Antidepressant use in bipolar disorder: continuing an age-old debate.Am J Psychiatry. 2010 Nov;167(11):1408; author reply 1408-9. doi: 10.1176/appi.ajp.2010.10040496. Am J Psychiatry. 2010. PMID: 21041258 No abstract available.
References
-
- American Psychiatric Association. Practice Guideline for the Treatment of Patients With Bipolar Disorder (Revision) Am J Psychiatry. 2002 April;(suppl):159. - PubMed
-
- Sachs GS, Printz DJ, Kahn DA, Carpenter D, Docherty JP. The Expert Consensus Guidelines: Medication Treatment of Bipolar Disorder, 2000: A Postgraduate Medicine Special Report. Columbus, Ohio: McGraw-Hill; 2000.
-
- Yatham LN, Kusumakar V, Parikh SV, Haslam DRS, Matte R, Sharma V, Kennedy S. Bipolar depression: treatment options. Can J Psychiatry. 1997;42(suppl 2):87S–91S. - PubMed
-
- Grunze H, Kasper S, Goodwin G, Bowden C, Baldwin D, Licht R, Vieta E, Möller HJ (World Federation of Societies of Biological Psychiatry Task Force on Treatment Guidelines for Bipolar Disorders) World Federation of Societies of Biological Psychiatry (WFSBP) guidelines for biological treatment of bipolar disorders, part I: treatment of bipolar depression. World J Biol Psychiatry. 2002;3:115–124. - PubMed
-
- Montgomery SA, Schatzberg AF, Guelfi JD, Kasper S, Nemeroff C, Swann A, Zajecka J. Pharmacotherapy of depression and mixed states in bipolar disorder. J Affect Disord. 2000;59(suppl 1):S39–S56. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

