The present and the future of neuroimaging in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis
- PMID: 20360339
- PMCID: PMC7964007
- DOI: 10.3174/ajnr.A2043
The present and the future of neuroimaging in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis
Abstract
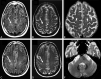
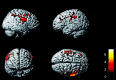
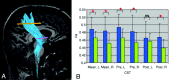
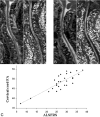
In patients with ALS, conventional MR imaging is frequently noninformative, and its use has been restricted to excluding other conditions that can mimic ALS. Conversely, the extensive application of modern MR imaging-based techniques to the study of ALS has undoubtedly improved our understanding of disease pathophysiology and is likely to have a role in the identification of potential biomarkers of disease progression. This review summarizes how new MR imaging technology is changing dramatically our understanding of the factors associated with ALS evolution and highlights the reasons why it should be used more extensively in studies of disease progression, including clinical trials.
Figures
References
-
- Dion PA, Daoud H, Rouleau GA. Genetics of motor neuron disorders: new insights into pathogenic mechanisms. Nat Rev Genet 2009;10:769–82 - PubMed
-
- Neumann M, Sampathu DM, Kwong LK, et al. Ubiquitinated TDP-43 in frontotemporal lobar degeneration and amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Science 2006;314:130–33 - PubMed
-
- Andersen PM, Borasio GD, Dengler R, et al. EFNS task force on management of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis: guidelines for diagnosing and clinical care of patients and relatives. Eur J Neurol 2005;12:921–38 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous
