Regulation of single-stranded DNA binding by the C termini of Escherichia coli single-stranded DNA-binding (SSB) protein
- PMID: 20360609
- PMCID: PMC2878057
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M110.118273
Regulation of single-stranded DNA binding by the C termini of Escherichia coli single-stranded DNA-binding (SSB) protein
Abstract
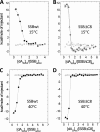
The homotetrameric Escherichia coli single-stranded DNA-binding (SSB) protein plays a central role in DNA replication, repair, and recombination. In addition to its essential activity of binding to transiently formed single-stranded (ss) DNA, SSB also binds an array of partner proteins and recruits them to their sites of action using its four intrinsically disordered C-terminal tails. Here we show that the binding of ssDNA to SSB is inhibited by the SSB C-terminal tails, specifically by the last 8 highly acidic amino acids that comprise the binding site for its multiple partner proteins. We examined the energetics of ssDNA binding to short oligodeoxynucleotides and find that at moderate salt concentration, removal of the acidic C-terminal ends increases the intrinsic affinity for ssDNA and enhances the negative cooperativity between ssDNA binding sites, indicating that the C termini exert an inhibitory effect on ssDNA binding. This inhibitory effect decreases as the salt concentration increases. Binding of ssDNA to approximately half of the SSB subunits relieves the inhibitory effect for all of the subunits. The inhibition by the C termini is due primarily to a less favorable entropy change upon ssDNA binding. These observations explain why ssDNA binding to SSB enhances the affinity of SSB for its partner proteins and suggest that the C termini of SSB may interact, at least transiently, with its ssDNA binding sites. This inhibition and its relief by ssDNA binding suggest a mechanism that enhances the ability of SSB to selectively recruit its partner proteins to sites on DNA.
Figures
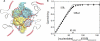

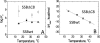

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

