N-myristoyltransferase inhibitors as new leads to treat sleeping sickness
- PMID: 20360736
- PMCID: PMC2917743
- DOI: 10.1038/nature08893
N-myristoyltransferase inhibitors as new leads to treat sleeping sickness
Abstract
African sleeping sickness or human African trypanosomiasis, caused by Trypanosoma brucei spp., is responsible for approximately 30,000 deaths each year. Available treatments for this disease are poor, with unacceptable efficacy and safety profiles, particularly in the late stage of the disease when the parasite has infected the central nervous system. Here we report the validation of a molecular target and the discovery of associated lead compounds with the potential to address this lack of suitable treatments. Inhibition of this target-T. brucei N-myristoyltransferase-leads to rapid killing of trypanosomes both in vitro and in vivo and cures trypanosomiasis in mice. These high-affinity inhibitors bind into the peptide substrate pocket of the enzyme and inhibit protein N-myristoylation in trypanosomes. The compounds identified have promising pharmaceutical properties and represent an opportunity to develop oral drugs to treat this devastating disease. Our studies validate T. brucei N-myristoyltransferase as a promising therapeutic target for human African trypanosomiasis.
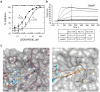
Figures
Comment in
-
Drug discovery: Fat-free proteins kill parasites.Nature. 2010 Apr 1;464(7289):689-90. doi: 10.1038/464689a. Nature. 2010. PMID: 20360728 No abstract available.
References
-
- Thuita JK, et al. Efficacy of the diamidine DB75 and its prodrug DB289, against murine models of human African trypanosomiasis. Acta Trop. 2008;108:6–10. - PubMed
-
- Raz B, et al. The Alamar Blue® assay to determine drug sensitivity of African trypanosomes (T.b.rhodesiense and T.b.gambiense) in vitro. Acta Trop. 1997;68:139–147. - PubMed
-
- Otwinowski Z, Minor W. Processing of X-ray diffraction data collected in oscillation mode. Methods Enzymol. 1997;276:307–326. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

