Specific functions of BIG1 and BIG2 in endomembrane organization
- PMID: 20360857
- PMCID: PMC2845624
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0009898
Specific functions of BIG1 and BIG2 in endomembrane organization
Abstract
Background: Transport of molecules from one subcellular compartment to another involves the recruitment of cytosolic coat protein complexes to a donor membrane to concentrate cargo, deform the membrane and ultimately to form an independent carrier. Small-GTP-binding proteins of the Arf family are central to many membrane trafficking events. Arfs are activated by guanine nucleotide exchange factors (GEFs) which results in their recruitment to membranes and subsequent engagement with Arf-effectors, many of which are coat proteins. Among the human BFA-sensitive large Arf-GEFs, the function of the two closely related BIG1 and BIG2 is still not clear, and recent studies have raised the question of functional redundancy between the two proteins.
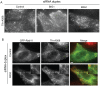
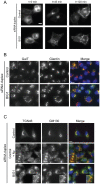
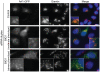
Methodology/principal findings: Here we have used small-interfering RNA on human cells and a combination of fixed and live-cell imaging to investigate the differential functions of BIG1 and BIG2 in endomembrane organization and function. Importantly, in this direct comparative study, we show discrete functions for BIG1 and BIG2. Our results show that depletion of BIG2 but not of BIG1 induces a tubulation of the recycling endosomal compartment, consistent with a specific role for BIG2 here. In contrast, suppression of BIG1 induces the formation of Golgi mini-stacks still polarized and functional in terms of cargo export.
Conclusions: A key finding from our work is that suppression of BIG1 expression results in a fragmentation of the Golgi apparatus. Our data indicate that the human BFA-sensitive large Arf-GEFs have non-redundant functions in cell organization and membrane trafficking. BIG1 is required to maintain the normal morphology of the Golgi; BIG2 is important for endosomal compartment integrity and cannot replace the function of BIG1 in Golgi organization.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures




Similar articles
-
The Sec7 guanine nucleotide exchange factor GBF1 regulates membrane recruitment of BIG1 and BIG2 guanine nucleotide exchange factors to the trans-Golgi network (TGN).J Biol Chem. 2013 Apr 19;288(16):11532-45. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M112.438481. Epub 2013 Feb 5. J Biol Chem. 2013. PMID: 23386609 Free PMC article.
-
Redundant roles of BIG2 and BIG1, guanine-nucleotide exchange factors for ADP-ribosylation factors in membrane traffic between the trans-Golgi network and endosomes.Mol Biol Cell. 2008 Jun;19(6):2650-60. doi: 10.1091/mbc.e07-10-1067. Epub 2008 Apr 16. Mol Biol Cell. 2008. PMID: 18417613 Free PMC article.
-
Association of brefeldin A-inhibited guanine nucleotide-exchange protein 2 (BIG2) with recycling endosomes during transferrin uptake.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2006 Feb 21;103(8):2635-40. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0510599103. Epub 2006 Feb 13. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2006. PMID: 16477018 Free PMC article.
-
Regulating the regulators: role of phosphorylation in modulating the function of the GBF1/BIG family of Sec7 ARF-GEFs.FEBS Lett. 2020 Jul;594(14):2213-2226. doi: 10.1002/1873-3468.13798. Epub 2020 May 14. FEBS Lett. 2020. PMID: 32333796 Review.
-
Allosteric regulation of Arf GTPases and their GEFs at the membrane interface.Small GTPases. 2016 Oct;7(4):283-296. doi: 10.1080/21541248.2016.1215778. Epub 2016 Jul 22. Small GTPases. 2016. PMID: 27449855 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
BIG1 is required for the survival of deep layer neurons, neuronal polarity, and the formation of axonal tracts between the thalamus and neocortex in developing brain.PLoS One. 2017 Apr 17;12(4):e0175888. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0175888. eCollection 2017. PLoS One. 2017. PMID: 28414797 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of cytoskeleton-associated proteins essential for lysosomal stability and survival of human cancer cells.PLoS One. 2012;7(10):e45381. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0045381. Epub 2012 Oct 11. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 23071517 Free PMC article.
-
Haploinsufficiency of ARFGEF1 is associated with developmental delay, intellectual disability, and epilepsy with variable expressivity.Genet Med. 2021 Oct;23(10):1901-1911. doi: 10.1038/s41436-021-01218-6. Epub 2021 Jun 10. Genet Med. 2021. PMID: 34113008
-
ARF family G proteins and their regulators: roles in membrane transport, development and disease.Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2011 Jun;12(6):362-75. doi: 10.1038/nrm3117. Epub 2011 May 18. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2011. PMID: 21587297 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Novel effects of Brefeldin A (BFA) in signaling through the insulin receptor (IR) pathway and regulating FoxO1-mediated transcription.Cell Logist. 2014 Jan 1;4(1):e27732. doi: 10.4161/cl.27732. Epub 2014 Jan 9. Cell Logist. 2014. PMID: 24843827 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bonifacino JS, Glick BS. The mechanisms of vesicle budding and fusion. Cell. 2004;116:153–166. - PubMed
-
- Duden R. ER-to-Golgi transport: COP I and COP II function. Molecular Membrane Biology. 2003;20:197–207. - PubMed
-
- Robinson MS. Adaptable adaptors for coated vesicles. Trends Cell Biol. 2004;14:167–174. - PubMed
-
- Gillingham AK, Munro S. The small g proteins of the arf family and their regulators. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol. 2007;23:579–611. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

