The extracellular matrix glycoprotein elastin microfibril interface located protein 2: a dual role in the tumor microenvironment
- PMID: 20360940
- PMCID: PMC2847737
- DOI: 10.1593/neo.91930
The extracellular matrix glycoprotein elastin microfibril interface located protein 2: a dual role in the tumor microenvironment
Abstract
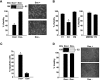
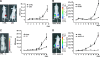
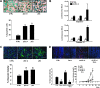
We have recently reported that elastin microfibril interface located protein 2 (EMILIN2), an extracellular matrix (ECM) glycoprotein, triggers cell death through a direct binding to death receptors. EMILIN2 thus influences cell viability through a mechanism that is unique for an ECM molecule. In the present work, we report an additional function for this molecule. First, we identify the region responsible for the proapoptotic effects, a 90-amino acid residue-long coiled-coil fragment toward the N-terminus of the molecule. The fragment recapitulates EMILIN2 proapoptotic mechanisms. In addition, using either the full molecule or the active fragment, for the first time, we demonstrate a significant antitumoral effect in vivo, likely due to a decrease in tumor cell viability. Unexpectedly, tumors treated with EMILIN2 or the deletion mutant display a significant increase of tumor angiogenesis. In view of this novel finding, the cotreatment of the growing tumors with an antiangiogenic drug led, in most cases, to a complete regression of tumor growth. These results grant further support to recent findings that pinpoint the microenvironment as an important regulator of cell fate under both physiological and pathological conditions and disclose the possibility of using EMILIN2 fragments as potent antineoplastic tools for cancer treatment.
Figures




Similar articles
-
EMILIN2 down-modulates the Wnt signalling pathway and suppresses breast cancer cell growth and migration.J Pathol. 2014 Mar;232(4):391-404. doi: 10.1002/path.4316. J Pathol. 2014. PMID: 24374807
-
Regulation of the extrinsic apoptotic pathway by the extracellular matrix glycoprotein EMILIN2.Mol Cell Biol. 2007 Oct;27(20):7176-87. doi: 10.1128/MCB.00696-07. Epub 2007 Aug 13. Mol Cell Biol. 2007. PMID: 17698584 Free PMC article.
-
Deregulated expression of Elastin Microfibril Interfacer 2 (EMILIN2) in gastric cancer affects tumor growth and angiogenesis.Matrix Biol Plus. 2020 Feb 19;6-7:100029. doi: 10.1016/j.mbplus.2020.100029. eCollection 2020 May. Matrix Biol Plus. 2020. PMID: 33543026 Free PMC article.
-
The ablation of the matricellular protein EMILIN2 causes defective vascularization due to impaired EGFR-dependent IL-8 production affecting tumor growth.Oncogene. 2018 Jun;37(25):3399-3414. doi: 10.1038/s41388-017-0107-x. Epub 2018 Feb 27. Oncogene. 2018. PMID: 29483644
-
[Mechanism of tumor cell-induced extracellular matrix degradation--inhibition of cell-surface proteolytic activity might have a therapeutic effect on tumor cell invasion and metastasis].Nihon Sanka Fujinka Gakkai Zasshi. 1996 Aug;48(8):623-32. Nihon Sanka Fujinka Gakkai Zasshi. 1996. PMID: 8808830 Review. Japanese.
Cited by
-
Extracellular Matrix: Emerging Roles and Potential Therapeutic Targets for Breast Cancer.Front Oncol. 2021 Apr 22;11:650453. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2021.650453. eCollection 2021. Front Oncol. 2021. PMID: 33968752 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Efficacy of Anti-PD-L1 Treatment in Melanoma Is Associated with the Expression of the ECM Molecule EMILIN2.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Jul 13;22(14):7511. doi: 10.3390/ijms22147511. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34299131 Free PMC article.
-
Research progress on the role of tumor‑associated macrophages in tumor development and their use as molecular targets (Review).Int J Oncol. 2024 Feb;64(2):11. doi: 10.3892/ijo.2023.5599. Epub 2023 Dec 8. Int J Oncol. 2024. PMID: 38063203 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The interconnectedness of cancer cell signaling.Neoplasia. 2011 Dec;13(12):1183-93. doi: 10.1593/neo.111746. Neoplasia. 2011. PMID: 22241964 Free PMC article.
-
Cancer associated fibroblasts: An essential role in the tumor microenvironment.Oncol Lett. 2017 Sep;14(3):2611-2620. doi: 10.3892/ol.2017.6497. Epub 2017 Jun 30. Oncol Lett. 2017. PMID: 28927027 Free PMC article.
References
Supplementary References
-
- Cha SS, Kim MS, Choi YH, Sung BJ, Shin NK, Shin HC, Sung YC, Oh BH. 2.8 A resolution crystal structure of human TRAIL, a cytokine with selective antitumor activity. Immunity. 1999;11:253–261. - PubMed
-
- Mongiat M, Mungiguerra G, Bot S, Mucignat MT, Giacomello E, Doliana R, Colombatti A. Self-assembly and supramolecular organization of EMILIN. J Biol Chem. 2000;275:25471–25480. - PubMed
-
- Mongkolsapaya J, Grimes JM, Chen N, Xu XN, Stuart DI, Jones EY, Screaton GR. Structure of the TRAIL-DR5 complex reveals mechanisms conferring specificity in apoptotic initiation. Nat Struct Biol. 1999;6:1048–1053. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
