AWBAT: early clinical experience
Abstract
Objective: The purpose of this article is to describe the early clinical experience with AWBAT.
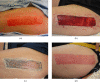
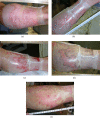
Methods: Burn patients requiring (1) donor sites or (2) treatment of a superficial burn wound injury were treated. A total of 45 patients with 69 distinct wounds were included. AWBAT-D was evaluated in donor sites and AWBAT-S was evaluated in superficial partial-thickness burns. Days to healing, pain, hematoma/seroma formation, and infection were noted. Ease of application, adherence, transparency, and physical adaptability details were collected.
Results: Average period to healing of donor sites treated with AWBAT-D (n=22 patients with n=26 wounds) was 11.2 days, sigma =1.95, with a range of 8-15 days and a median of 11 days. Pain rating at 24 hours was 1.2, sigma =0.43 (n=18) and at 48 hours mean was 1.2, sigma =0.46 (n=15). Average period to healing of superficial burns treated with AWBAT-S (n=15 patients with n=18 wounds) was 8.1 days, sigma =2.48, with a range of 5-13 days and a median of 7 days. Pain rating at 24 hours was 1.5, sigma =0.85 (n=10) and at 48 hours mean was 1.75, sigma =0.89 (n=8). There was zero incidence of hematoma/seroma. No infections were seen. Results indicate that AWBAT was easily applied with good initial adherence. It was noted to be transparent, conformant, and pliable.
Discussion: Early experience demonstrates that AWBAT performs well on donor sites and superficial partial-thickness burns and delivers the desired attributes of a temporary skin substitute including good adherence, infection control, transparency, adapatability, and pain control.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The Search for an Ideal Temporary Skin Substitute: AWBAT Plus, a Combination Product Wound Dressing Medical Device.Eplasty. 2010 Sep 15;10:e60. Eplasty. 2010. PMID: 20862296 Free PMC article.
-
A Randomized, Prospective Study of the Treatment of Superficial Partial-Thickness Burns: AWBAT-S Versus Biobrane.Eplasty. 2011 Feb 24;11:e10. Eplasty. 2011. PMID: 21369369 Free PMC article.
-
A randomised prospective study of split skin graft donor site dressings: AWBAT-D™ vs. Duoderm®.Burns. 2012 Sep;38(6):889-98. doi: 10.1016/j.burns.2011.12.022. Epub 2012 Feb 23. Burns. 2012. PMID: 22365615 Clinical Trial.
-
Use of a copolymer dressing on superficial and partial-thickness burns in a paediatric population.J Wound Care. 2015 Jul;24(7):S4-8. doi: 10.12968/jowc.2015.24.Sup7.S4. J Wound Care. 2015. PMID: 26198721
-
Burn wounds: infection and healing.Am J Surg. 1994 Jan;167(1A):46S-48S. doi: 10.1016/0002-9610(94)90011-6. Am J Surg. 1994. PMID: 8109685 Review.
Cited by
-
The Search for an Ideal Temporary Skin Substitute: AWBAT Plus, a Combination Product Wound Dressing Medical Device.Eplasty. 2010 Sep 15;10:e60. Eplasty. 2010. PMID: 20862296 Free PMC article.
-
Effectiveness of collagen/oxidised regenerated cellulose/silver-containing composite wound dressing for the treatment of medium-depth split-thickness skin graft donor site wounds in multi-morbid patients: a prospective, non-comparative, single-centre study.Int Wound J. 2017 Oct;14(5):791-800. doi: 10.1111/iwj.12698. Epub 2016 Dec 1. Int Wound J. 2017. PMID: 27905181 Free PMC article.
-
Evolution of a Biosynthetic Temporary Skin Substitute: A Preliminary Study.Eplasty. 2015 Jul 20;15:e30. eCollection 2015. Eplasty. 2015. PMID: 26229573 Free PMC article.
-
Wound Coverage Technologies in Burn Care: Established Techniques.J Burn Care Res. 2018 Apr 20;39(3):313-318. doi: 10.1097/BCR.0b013e3182920d29. J Burn Care Res. 2018. PMID: 24165670 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Ehrenreich M, Ruszczak Z. Update on tissue-engineered biological dressing. Tissue Eng. 2006;12(9):2407. - PubMed
-
- Pruitt BA, Levine NS. Characteristics and uses of biologic dressings and skin substitutes. Arch Surg. 1984;119:312. - PubMed
-
- Smith DJ., Jr Use of Biobrane in wound management. J Burn Care Rehabil. 1995;16:317. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
