One-Day vs Two-Day Epidural Analgesia for Total Knee Arthroplasty (TKA): A Retrospective Cohort Study
- PMID: 20361034
- PMCID: PMC2847206
- DOI: 10.2174/1874325001004010031
One-Day vs Two-Day Epidural Analgesia for Total Knee Arthroplasty (TKA): A Retrospective Cohort Study
Abstract
Introduction: Over 500,000 total knee arthroplasties (TKAs) are performed annually in the US, yet postoperative pain management varies widely. In patients managed with epidural analgesia, the epidural catheter is generally removed on the second postoperative day. We compared in-hospital outcomes associated with removing the epidural catheter on postoperative day 1 (POD1-group) vs on postoperative day 2 (POD2-group) among patients undergoing TKA.
Methods: We identified 89 patients who had TKA performed by a single surgeon from January through July 2007, and who were managed with epidural analgesia. This study took advantage of a change of policy from removing the epidural on the second postoperative day prior to March 2007 (n = 34) to removing the epidural on the first postoperative day thereafter (n = 55). Data were obtained by medical record review and analyzed with bivariate and multivariate techniques. Outcomes included knee range of motion (ROM), pain (0-10 scale), distance walked, narcotic usage, and length of stay.
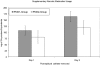
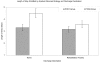
Results: The mean patient age was 68 +/- 10 years. We did not identify clinically important differences in preoperative characteristics across groups. Patients in the POD1- group had a shorter length of stay (median of 3 vs 4 days in the POD2-group, p<0.001). The POD1-group also walked a greater distance on the second postoperative day (mean of 38 feet vs 9 feet in the POD2-group, p < 0.002). We did not observe a difference between the two groups with respect to change in passive ROM, pain on the second postoperative day, or narcotic usage. The POD1-group had more restricted continuous passive motion settings on the second postoperative day than the POD2-group (50 degrees vs 65 degrees , p = 0.031), and the POD1-group had somewhat worse passive range of motion at discharge (e.g. passive flexion 82o vs 76o in the POD2- group, p = 0.078).
Conclusion: The balance between a shorter hospital stay and earlier walking achievement with the POD1-strategy-- vs better ROM at the time of discharge with the POD2-strategy-- should be considered when planning TKA pain management. These results should be confirmed with longer term studies and randomized designs. EVIDENCE LEVEL III: Retrospective comparative study.
Keywords: Knee; analgesia.; arthroplasty.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The Impact of Early Epidural Discontinuation on Pain, Opioid Usage, and Length of Stay After Periacetabular Osteotomy.J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2020 Nov 4;102(Suppl 2):59-65. doi: 10.2106/JBJS.19.01405. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2020. PMID: 32530876
-
Tranexamic Acid Effectively Reduces Blood Loss and Transfusion Rates during Simultaneous Bilateral Total Knee Arthroplasty.J Knee Surg. 2018 Mar;31(3):270-276. doi: 10.1055/s-0037-1603333. Epub 2017 May 15. J Knee Surg. 2018. PMID: 28505683
-
Use of drop and dangle rehabilitation protocol to increase knee flexion following total knee arthroplasty: a comparison with continuous passive motion machine.J Med Assoc Thai. 2014 Sep;97 Suppl 9:S16-22. J Med Assoc Thai. 2014. PMID: 25365884
-
The efficacy and safety of perioperative glucocorticoid for total knee arthroplasty: a systematic review and meta-analysis.BMC Anesthesiol. 2024 Apr 15;24(1):144. doi: 10.1186/s12871-024-02530-9. BMC Anesthesiol. 2024. PMID: 38622510 Free PMC article.
-
Efficacy of Additional Corticosteroid in a Multimodal Cocktail for Postoperative Analgesia Following Total Knee Arthroplasty: A Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials.Pain Pract. 2019 Mar;19(3):316-327. doi: 10.1111/papr.12740. Epub 2019 Jan 1. Pain Pract. 2019. PMID: 30354013 Review.
Cited by
-
Continuous femoral nerve block is more effective than continuous adductor canal block for treating pain after total knee arthroplasty: A randomized, double-blind, controlled trial.Medicine (Baltimore). 2019 Sep;98(39):e17358. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000017358. Medicine (Baltimore). 2019. PMID: 31574881 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
References
-
- Kurtz S, Ong K, Lau E, Mowat F, Halpern M. Projections of primary and revision hip and knee arthroplasty in the United States from 2005 to 2030. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2007;89(4):780–5. - PubMed
-
- Kurtz S, Mowat F, Ong K, Chan N, Lau E, Halpern M. Prevalence of primary and revision total hip and knee arthroplasty in the United States from 1990 through 2002. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2005;87(7):1487–97. - PubMed
-
- Singelyn FJ, Deyaert M, Joris D, Pendeville E, Gouverneur JM. Effects of intravenous patient-controlled analgesia with morphine, continuous epidural analgesia, and continuous three-in-one block on postoperative pain and knee rehabilitation after unilateral total knee arthroplasty. Anesth Analg. 1998;87(1):88–92. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
