The primary cilium as a Hedgehog signal transduction machine
- PMID: 20362092
- PMCID: PMC2867239
- DOI: 10.1016/S0091-679X(08)94010-3
The primary cilium as a Hedgehog signal transduction machine
Abstract
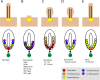
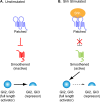
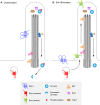
The Hedgehog (Hh) signal transduction pathway is essential for the development and patterning of numerous organ systems, and has important roles in a variety of human cancers. Genetic screens for mouse embryonic patterning mutants first showed a connection between mammalian Hh signaling and intraflagellar transport (IFT), a process required for construction of the primary cilium, a small cellular projection found on most vertebrate cells. Additional genetic and cell biological studies have provided very strong evidence that mammalian Hh signaling depends on the primary cilium. Here, we review the evidence that defines the integral roles that IFT proteins and cilia play in the regulation of the Hh signal transduction pathway in vertebrates. We discuss the mechanisms that control localization of Hh pathway proteins to the cilium, focusing on the transmembrane protein Smoothened (Smo), which moves into the cilium in response to Hh ligand. The phenotypes caused by loss of cilia-associated proteins are complex, which suggests that cilia and IFT play active roles in mediating Hh signaling rather than serving simply as a compartment in which pathway components are concentrated. Hh signaling in Drosophila does not depend on cilia, but there appear to be ancient links between cilia and components of the Hh pathway that may reveal how this fundamental difference between the Drosophila and mammalian Hh pathways arose in evolution.
2009 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Intraflagellar transport, cilia, and mammalian Hedgehog signaling: analysis in mouse embryonic fibroblasts.Dev Dyn. 2008 Aug;237(8):2030-8. doi: 10.1002/dvdy.21551. Dev Dyn. 2008. PMID: 18488998 Free PMC article.
-
Kinetics of hedgehog-dependent full-length Gli3 accumulation in primary cilia and subsequent degradation.Mol Cell Biol. 2010 Apr;30(8):1910-22. doi: 10.1128/MCB.01089-09. Epub 2010 Feb 12. Mol Cell Biol. 2010. PMID: 20154143 Free PMC article.
-
Intraflagellar transport 27 is essential for hedgehog signaling but dispensable for ciliogenesis during hair follicle morphogenesis.Development. 2015 Jun 15;142(12):2194-202. doi: 10.1242/dev.115261. Epub 2015 May 28. Development. 2015. PMID: 26023097 Free PMC article.
-
Cilia and developmental signaling.Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol. 2007;23:345-73. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cellbio.23.090506.123249. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol. 2007. PMID: 17506691 Free PMC article. Review.
-
G-protein-coupled receptors, Hedgehog signaling and primary cilia.Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2014 Sep;33:63-72. doi: 10.1016/j.semcdb.2014.05.002. Epub 2014 May 17. Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2014. PMID: 24845016 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The activity of Gli transcription factors is essential for Kras-induced pancreatic tumorigenesis.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2012 Apr 24;109(17):E1038-47. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1114168109. Epub 2012 Apr 9. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2012. PMID: 22493246 Free PMC article.
-
SUMOylation Blocks the Ubiquitin-Mediated Degradation of the Nephronophthisis Gene Product Glis2/NPHP7.PLoS One. 2015 Jun 17;10(6):e0130275. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0130275. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 26083374 Free PMC article.
-
STIL Acts as an Oncogenetic Driver in a Primary Cilia-Dependent Manner in Human Cancer.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2022 Jan 26;10:804419. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2022.804419. eCollection 2022. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2022. PMID: 35155425 Free PMC article.
-
Microscopy-Based Automated Live Cell Screening for Small Molecules That Affect Ciliation.Front Genet. 2019 Feb 12;10:75. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2019.00075. eCollection 2019. Front Genet. 2019. PMID: 30809247 Free PMC article.
-
Roles of Primary Cilia in the Developing Brain.Front Cell Neurosci. 2019 May 14;13:218. doi: 10.3389/fncel.2019.00218. eCollection 2019. Front Cell Neurosci. 2019. PMID: 31139054 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Appel B, Eisen JS. Retinoids run rampant: multiple roles during spinal cord and motor neuron development. Neuron. 2003;40:461–4. - PubMed
-
- Aza-Blanc P, et al. Proteolysis that is inhibited by hedgehog targets Cubitus interruptus protein to the nucleus and converts it to a repressor. Cell. 1997;89:1043–53. - PubMed
-
- Badano JL, et al. The ciliopathies: an emerging class of human genetic disorders. Annu Rev Genomics Hum Genet. 2006;7:125–48. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

