Crumbs regulates Salvador/Warts/Hippo signaling in Drosophila via the FERM-domain protein Expanded
- PMID: 20362445
- PMCID: PMC2855393
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cub.2010.03.019
Crumbs regulates Salvador/Warts/Hippo signaling in Drosophila via the FERM-domain protein Expanded
Abstract
Background: Altered expression of apicobasal polarity factors is associated with cancer in vertebrates and tissue overgrowth in invertebrates, yet the mechanisms by which these factors affect growth-regulatory pathways are not well defined. We have tested the basis of an overgrowth phenotype driven by the Drosophila protein Crumbs (Crb), which nucleates an apical membrane complex that functionally interacts with the Par6/Par3/aPKC and Scrib/Dlg/Lgl apicobasal polarity complexes.
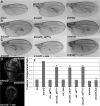
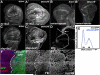
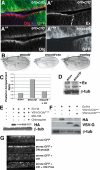
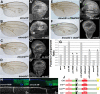
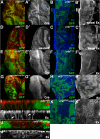
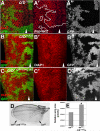
Results: We find that Crb-driven growth is dependent upon the Salvador/Warts/Hippo (SWH) pathway and its transcriptional effector Yorkie (Yki). Expression of the Crb intracellular domain elevates Yki activity, and this correlates in tissues and cultured cells with loss of Expanded (Ex), an apically localized SWH component that inhibits Yki. Reciprocally, loss of crb elevates Ex levels, although this excess Ex does not concentrate to its normal location at apical junctions. The Ex-regulatory domain of Crb maps to the juxtamembrane FERM-binding motif (JM), a cytoskeletal interaction domain distinct from the PDZ-binding motif (PBM) through which Crb binds polarity factors. Expression of Crb-JM drives Yki activity and organ growth with little effect on tissue architecture, while Crb-PBM reciprocally produces tissue architectural defects without significant effect on Yki activity.
Conclusions: These studies identify Crb as a novel SWH regulator via JM-dependent effects on Ex levels and localization and suggest that discrete domains within Crb may allow it to integrate junctional polarity signals with a conserved growth pathway.
Figures
Comment in
-
Signalling: Regulation and crosstalk.Nat Rev Cancer. 2010 Jun;10(6):386. doi: 10.1038/nrc2864. Nat Rev Cancer. 2010. PMID: 20509173 No abstract available.
References
-
- Bilder D. Epithelial polarity and proliferation control: links from the Drosophila neoplastic tumor suppressors. Genes Dev. 2004;18:1909–1925. - PubMed
-
- Humbert PO, Grzeschik NA, Brumby AM, Galea R, Elsum I, Richardson HE. Control of tumourigenesis by the Scribble/Dlg/Lgl polarity module. Oncogene. 2008;27:6888–6907. - PubMed
-
- Wodarz A, Hinz U, Engelbert M, Knust E. Expression of crumbs confers apical character on plasma membrane domains of ectodermal epithelia of Drosophila. Cell. 1995;82:67–76. - PubMed
-
- Lu H, Bilder D. Endocytic control of epithelial polarity and proliferation in Drosophila. Nat Cell Biol. 2005;7:1132–1139. - PubMed
-
- Moberg KH, Schelble S, Burdick SK, Hariharan IK. Mutations in erupted, the Drosophila ortholog of mammalian tumor susceptibility gene 101, elicit non-cell-autonomous overgrowth. Dev Cell. 2005;9:699–710. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

