Vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF)-A: role on cardiac angiogenesis following myocardial infarction
- PMID: 20362592
- PMCID: PMC3628688
- DOI: 10.1016/j.mvr.2010.03.014
Vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF)-A: role on cardiac angiogenesis following myocardial infarction
Abstract
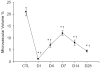
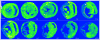
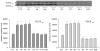
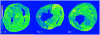
The current study is to determine the regulatory role of VEGF-A in cardiac angiogenesis following myocardial infarction (MI). Cardiac angiogenic response and temporal/spatial expression of VEGF-A/VEGF receptors (VEGFR) were examined at 1, 2, 6, 12 h and 1, 2, 3, 4, 7, 14, and 28 days postMI. We found that following MI, newly formed vessels first appeared at the border zone between noninfarcted and infarcted myocardium as early as day 3 and subsequently in the infarcted myocardium. Vascular density in the infarcted myocardium peaked at day 7 and then gradually declined. VEGF-A mRNA started to increase at the border zone at 2 h postMI, reached peak at 12 h, declined at day 1, and returned to normal levels at day 2 and thereafter. VEGF-A protein levels at the border zone were only increased during day 1 postMI. VEGF-A within the infarcted myocardium levels, however, was persistently suppressed postMI. VEGFR expression was significantly increased only at the border zone at day 1, but not in the later stages. The expression of VEGF-A/VEGFR remained unchanged in the noninfarcted myocardium. Thus, the early rise of VEGF-A/VEGFR at the border zone suggests that VEGF-A initiates the cardiac angiogenic response postMI, but short-lived VEGF-A/VEGFR activation at the border zone and consistently suppressed VEGF-A within the infarcted myocardium suggests that VEGF-A may not be crucial to the later stages of angiogenesis.
Copyright 2010. Published by Elsevier Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
Authors have no conflicts of interest to disclose.
Figures

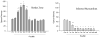
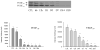
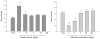
References
-
- Ahn A, et al. Therapeutic angiogenesis: a new treatment approach for ischemic heart disease--Part II. Cardiol Rev. 2008;16:219–29. - PubMed
-
- Barandon L, et al. Frizzled A, a novel angiogenic factor: promises for cardiac repair. Eur J Cardiothorac Surg. 2004;25:76–83. - PubMed
-
- Boodhwani M, et al. The future of therapeutic myocardial angiogenesis. Shock. 2006;26:332–41. - PubMed
-
- Cooper ME, et al. Increased renal expression of vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) and its receptor VEGFR-2 in experimental diabetes. Diabetes. 1999;48:2229–39. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

