C-type lectin DC-SIGN: an adhesion, signalling and antigen-uptake molecule that guides dendritic cells in immunity
- PMID: 20363321
- PMCID: PMC7127357
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cellsig.2010.03.018
C-type lectin DC-SIGN: an adhesion, signalling and antigen-uptake molecule that guides dendritic cells in immunity
Abstract
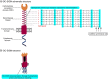
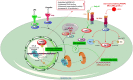
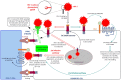
The dendritic cell-specific intercellular adhesion molecule-3-grabbing non-integrin (DC-SIGN) is a type II C-type lectin whose expression is restricted to the most potent antigen-presenting cells (APCs), the dendritic cells (DCs). In recent years, DC-SIGN has gained an exponential increase in attention because of its involvement in multiple aspects of immune function. Besides being an adhesion molecule, particularly in binding ICAM-2 and ICAM-3, it is also crucial in recognizing several endogenous and exogenous antigens. Additionally, the intracellular domain of DC-SIGN includes molecular motifs, which enable the activation of signal transduction pathways involving Raf-1 and subsequent modulation of DC-maturation status, through direct modification of nuclear factor Nf-kappaB in DCs. Upon DC-SIGN engagement by mannose- or fucose-containing oligosaccharides, the latter leads to a tailored Toll-like receptor signalling, resulting in an altered DC-cytokine profile and skewing of Th1/Th2 responses. In this article, we will discuss recent advances on a broad perspective concerning DC-SIGN structure, signalling and immune function.
Copyright 2010 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
References
-
- Banchereau J., Briere F., Caux C., Davoust J., Lebecque S., Liu Y.J., Pulendran B., Palucka K. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 2000;18:767. - PubMed
-
- Geijtenbeek T.B., Torensma R., van Vliet S.J., van Duijnhoven G.C., Adema G.J., van Kooyk Y., Figdor C.G. Cell. 2000;100(5):575. - PubMed
-
- Figdor C.G., van Kooyk Y., Adema G.J. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2002;2(2):77. - PubMed
-
- Tacken P.J., de Vries I.J., Gijzen K., Joosten B., Wu D., Rother R.P., Faas S.J., Punt C.J., Torensma R., Adema G.J., Figdor C.G. Blood. 2005;106(4):1278. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

