Role of extracellular DNA in initial bacterial adhesion and surface aggregation
- PMID: 20363802
- PMCID: PMC2869138
- DOI: 10.1128/AEM.03119-09
Role of extracellular DNA in initial bacterial adhesion and surface aggregation
Abstract
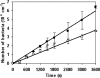
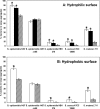
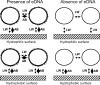
Extracellular DNA (eDNA) is an important component of the biofilm matrix. We show that removal of eDNA from Gram-positive bacteria reduces initial adhesion to and aggregation of bacteria on surfaces. Thermodynamic analyses indicated that eDNA introduces favorable acid-base interactions, explaining the effect of eDNA on aggregation and adhesion to the surface.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The roles of extracellular DNA in the structural integrity of extracellular polymeric substance and bacterial biofilm development.Environ Microbiol Rep. 2013 Dec;5(6):778-86. doi: 10.1111/1758-2229.12085. Epub 2013 Jul 25. Environ Microbiol Rep. 2013. PMID: 24249286 Review.
-
The role of extracellular DNA in the establishment, maintenance and perpetuation of bacterial biofilms.Crit Rev Microbiol. 2015;41(3):341-52. doi: 10.3109/1040841X.2013.841639. Epub 2013 Dec 4. Crit Rev Microbiol. 2015. PMID: 24303798 Review.
-
Emergent Properties in Streptococcus mutans Biofilms Are Controlled through Adhesion Force Sensing by Initial Colonizers.mBio. 2019 Sep 10;10(5):e01908-19. doi: 10.1128/mBio.01908-19. mBio. 2019. PMID: 31506311 Free PMC article.
-
Surface physicochemistry and ionic strength affects eDNA's role in bacterial adhesion to abiotic surfaces.PLoS One. 2014 Aug 14;9(8):e105033. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0105033. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 25122477 Free PMC article.
-
Influence of calcium in extracellular DNA mediated bacterial aggregation and biofilm formation.PLoS One. 2014 Mar 20;9(3):e91935. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0091935. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 24651318 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Presence of Extracellular DNA during Biofilm Formation by Xanthomonas citri subsp. citri Strains with Different Host Range.PLoS One. 2016 Jun 1;11(6):e0156695. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0156695. eCollection 2016. PLoS One. 2016. PMID: 27248687 Free PMC article.
-
The role of bacterial biofilms and surface components in plant-bacterial associations.Int J Mol Sci. 2013 Jul 30;14(8):15838-59. doi: 10.3390/ijms140815838. Int J Mol Sci. 2013. PMID: 23903045 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Extracellular DNA within a nontypeable Haemophilus influenzae-induced biofilm binds human beta defensin-3 and reduces its antimicrobial activity.J Innate Immun. 2013;5(1):24-38. doi: 10.1159/000339961. Epub 2012 Aug 22. J Innate Immun. 2013. PMID: 22922323 Free PMC article.
-
Role of SCFAs for Fimbrillin-Dependent Biofilm Formation of Actinomyces oris.Microorganisms. 2018 Nov 13;6(4):114. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms6040114. Microorganisms. 2018. PMID: 30428566 Free PMC article.
-
Precision Design of Antimicrobial Surfaces.Front Med Technol. 2021 Feb 16;3:640929. doi: 10.3389/fmedt.2021.640929. eCollection 2021. Front Med Technol. 2021. PMID: 35047910 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Abu-Lail, N. I., and T. A. Camesano. 2006. Specific and nonspecific interaction forces between Escherichia coli and silicon nitride, determined by Poisson statistical analysis. Langmuir 22:7296-7301. - PubMed
-
- Allesen-Holm, M., K. B. Barken, L. Yang, M. Klausen, J. S. Webb, S. Kjelleberg, S. Molin, M. Givskov, and T. Tolker-Nielsen. 2006. A characterization of DNA release in Pseudomonas aeruginosa cultures and biofilms. Mol. Microbiol. 59:1114-1128. - PubMed
-
- Battin, T. J., W. T. Sloan, S. Kjelleberg, H. Daims, I. M. Head, T. P. Curtis, and L. Eberl. 2007. Microbial landscapes: new paths to biofilm research. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 5:76-81. - PubMed
-
- Boks, N. P., W. Norde, H. C. van der Mei, and H. J. Busscher. 2008. Forces involved in bacterial adhesion to hydrophilic and hydrophobic surfaces. Microbiology 154:3122-3133. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

