Genetic, structural, and antigenic analyses of glycan diversity in the O-linked protein glycosylation systems of human Neisseria species
- PMID: 20363948
- PMCID: PMC2876500
- DOI: 10.1128/JB.00101-10
Genetic, structural, and antigenic analyses of glycan diversity in the O-linked protein glycosylation systems of human Neisseria species
Abstract
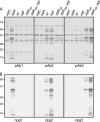
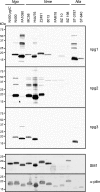
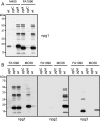
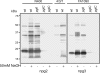
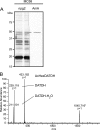
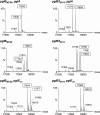
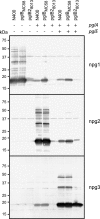
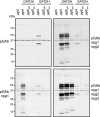
Bacterial capsular polysaccharides and lipopolysaccharides are well-established ligands of innate and adaptive immune effectors and often exhibit structural and antigenic variability. Although many surface-localized glycoproteins have been identified in bacterial pathogens and symbionts, it not clear if and how selection impacts associated glycoform structure. Here, a systematic approach was devised to correlate gene repertoire with protein-associated glycoform structure in Neisseria species important to human health and disease. By manipulating the protein glycosylation (pgl) gene content and assessing the glycan structure by mass spectrometry and reactivity with monoclonal antibodies, it was established that protein-associated glycans are antigenically variable and that at least nine distinct glycoforms can be expressed in vitro. These studies also revealed that in addition to Neisseria gonorrhoeae strain N400, one other gonococcal strain and isolates of Neisseria meningitidis and Neisseria lactamica exhibit broad-spectrum O-linked protein glycosylation. Although a strong correlation between pgl gene content, glycoform expression, and serological profile was observed, there were significant exceptions, particularly with regard to levels of microheterogeneity. This work provides a technological platform for molecular serotyping of neisserial protein glycans and for elucidating pgl gene evolution.
Figures
References
-
- Aas, F. E., W. Egge-Jacobsen, H. C. Winther-Larsen, C. Lovold, P. G. Hitchen, A. Dell, and M. Koomey. 2006. Neisseria gonorrhoeae type IV pili undergo multisite, hierarchical modifications with phosphoethanolamine and phosphocholine requiring an enzyme structurally related to lipopolysaccharide phosphoethanolamine transferases. J. Biol. Chem. 281:27712-27723. - PubMed
-
- Aas, F. E., H. C. Winther-Larsen, M. Wolfgang, S. Frye, C. Lovold, N. Roos, J. P. van Putten, and M. Koomey. 2007. Substitutions in the N-terminal alpha helical spine of Neisseria gonorrhoeae pilin affect type IV pilus assembly, dynamics and associated functions. Mol. Microbiol. 63:69-85. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

