Stress-induced synthesis of phosphatidylinositol 3-phosphate in mycobacteria
- PMID: 20364020
- PMCID: PMC2878017
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M110.119263
Stress-induced synthesis of phosphatidylinositol 3-phosphate in mycobacteria
Abstract
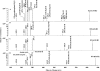
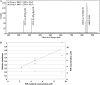
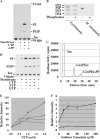
Phosphoinositides play key roles in regulating membrane dynamics and intracellular signaling in eukaryotic cells. However, comparable lipid-based signaling pathways have not been identified in bacteria. Here we show that Mycobacterium smegmatis and other Actinomycetes bacteria can synthesize the phosphoinositide, phosphatidylinositol 3-phosphate (PI3P). This lipid was transiently labeled with [(3)H]inositol. Sensitivity of the purified lipid to alkaline phosphatase, headgroup analysis by high-pressure liquid chromatography, and mass spectrometry demonstrated that it had the structure 1,2-[tuberculostearoyl, octadecenoyl]-sn-glycero 3-phosphoinositol 3-phosphate. Synthesis of PI3P was elevated by salt stress but not by exposure to high concentrations of non-ionic solutes. Synthesis of PI3P in a cell-free system was stimulated by the synthesis of CDP-diacylglycerol, a lipid substrate for phosphatidylinositol (PI) biosynthesis, suggesting that efficient cell-free PI3P synthesis is dependent on de novo PI synthesis. In vitro experiments further indicated that the rapid turnover of this lipid was mediated, at least in part, by a vanadate-sensitive phosphatase. This is the first example of de novo synthesis of PI3P in bacteria, and the transient synthesis in response to environmental stimuli suggests that some bacteria may have evolved similar lipid-mediated signaling pathways to those observed in eukaryotic cells.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Phosphatidylinositol synthesis in mycobacteria.Biochim Biophys Acta. 1999 Jan 4;1436(3):437-50. doi: 10.1016/s0005-2760(98)00151-9. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1999. PMID: 9989274
-
A revised biosynthetic pathway for phosphatidylinositol in Mycobacteria.J Biochem. 2010 Nov;148(5):593-602. doi: 10.1093/jb/mvq093. Epub 2010 Aug 26. J Biochem. 2010. PMID: 20798167
-
Ionization properties of phosphatidylinositol polyphosphates in mixed model membranes.Biochemistry. 2009 Oct 13;48(40):9360-71. doi: 10.1021/bi9008616. Biochemistry. 2009. PMID: 19725516
-
Phosphoinositides, Major Actors in Membrane Trafficking and Lipid Signaling Pathways.Int J Mol Sci. 2017 Mar 15;18(3):634. doi: 10.3390/ijms18030634. Int J Mol Sci. 2017. PMID: 28294977 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Phosphatidylinositol-3-phosphate in the regulation of autophagy membrane dynamics.FEBS J. 2017 May;284(9):1267-1278. doi: 10.1111/febs.13987. Epub 2017 Jan 5. FEBS J. 2017. PMID: 27973739 Review.
Cited by
-
The cell envelope-associated phospholipid-binding protein LmeA is required for mannan polymerization in mycobacteria.J Biol Chem. 2017 Oct 20;292(42):17407-17417. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M117.804377. Epub 2017 Aug 29. J Biol Chem. 2017. PMID: 28855252 Free PMC article.
-
Intoxication of host cells by the T3SS phospholipase ExoU: PI(4,5)P2-associated, cytoskeletal collapse and late phase membrane blebbing.PLoS One. 2014 Jul 25;9(7):e103127. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0103127. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 25061861 Free PMC article.
-
Phosphoinositides: tiny lipids with giant impact on cell regulation.Physiol Rev. 2013 Jul;93(3):1019-137. doi: 10.1152/physrev.00028.2012. Physiol Rev. 2013. PMID: 23899561 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Comprehensive lipidomic analysis of the genus Cutibacterium.mSphere. 2024 May 29;9(5):e0005424. doi: 10.1128/msphere.00054-24. Epub 2024 May 7. mSphere. 2024. PMID: 38712970 Free PMC article.
-
Vibrio cholerae requires the type VI secretion system virulence factor VasX to kill Dictyostelium discoideum.Infect Immun. 2011 Jul;79(7):2941-9. doi: 10.1128/IAI.01266-10. Epub 2011 May 9. Infect Immun. 2011. PMID: 21555399 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Whitman M., Downes C. P., Keeler M., Keller T., Cantley L. (1988) Nature 332, 644–646 - PubMed
-
- Falasca M., Maffucci T. (2006) Arch. Physiol. Biochem. 112, 274–284 - PubMed
-
- Lindmo K., Stenmark H. (2006) J. Cell Sci. 119, 605–614 - PubMed
-
- Engelman J. A., Luo J., Cantley L. C. (2006) Nat. Rev. Genet. 7, 606–619 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

