Mechanisms of oxidative protein folding in the bacterial cell envelope
- PMID: 20367276
- PMCID: PMC2959184
- DOI: 10.1089/ars.2010.3187
Mechanisms of oxidative protein folding in the bacterial cell envelope
Abstract
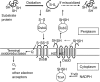
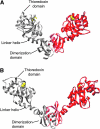
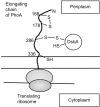
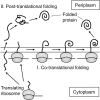
Disulfide-bond formation is important for the correct folding of a great number of proteins that are exported to the cell envelope of bacteria. Bacterial cells have evolved elaborate systems to promote the joining of two cysteines to form a disulfide bond and to repair misoxidized proteins. In the past two decades, significant advances have occurred in our understanding of the enzyme systems (DsbA, DsbB, DsbC, DsbG, and DsbD) used by the gram-negative bacterium Escherichia coli to ensure that correct pairs of cysteines are joined during the process of protein folding. However, a number of fundamental questions about these processes remain, especially about how they occur inside the cell. In addition, recent recognition of the increasing diversity among bacteria in the disulfide bond-forming capacity and in the systems for introducing disulfide bonds into proteins is raising new questions. We review here the marked progress in this field and discuss important questions that remain for future studies.
Figures
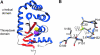
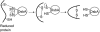
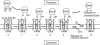
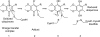
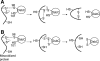
References
-
- Andersen CL. Matthey-Dupraz A. Missiakas D. Raina S. A new Escherichia coli gene, dsbG, encodes a periplasmic protein involved in disulphide bond formation, required for recycling DsbA/DsbB and DsbC redox proteins. Mol Microbiol. 1997;26:121–132. - PubMed
-
- Åslund F. Berndt KD. Holmgren A. Redox potentials of glutaredoxins and other thiol-disulfide oxidoreductases of the thioredoxin superfamily determined by direct protein-protein redox equilibria. J Biol Chem. 1997;272:30780–30786. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

