Bi-directional calcium signaling between adjacent leukocytes and trophoblast-like cells
- PMID: 20367627
- PMCID: PMC3059506
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1600-0897.2010.00839.x
Bi-directional calcium signaling between adjacent leukocytes and trophoblast-like cells
Abstract
Problem: Trophoblasts are believed to play an important role in mitigating immunological responses against the fetus. To better understand the nature of trophoblast-leukocyte interactions, we have studied signal transduction during intercellular interactions.
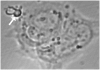
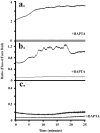
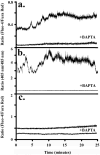
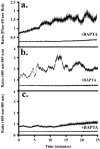
Method of study: Using a highly sensitive microfluorometric ratioing method and Ca²(+) -sensitive dyes, we measured Ca²(+) signals in trophoblast-like cell lines (JEG-3 and JAR) or in leukocytes (neutrophils and monocytes) during intercellular contact.
Results: Trophoblast cell lines exhibit Ca²(+) signals during leukocyte contact. In contrast, leukocytes cannot elicit Ca²(+) signals in non-opsonized tumour cells, suggesting that Ca²(+) signaling is not a general feature of cell-cell encounters. Similarly, leukocytes demonstrate Ca²(+) signals during contact with trophoblast cell lines. Ca²(+) signals were confirmed using three dyes and with the Ca²(+) buffer BAPTA.
Conclusion: We suggest that leukocyte-to-trophoblast interactions lead to mutual Ca²(+) signaling events in both cell types, which may contribute to immunoregulation at the materno-fetal interface.
© 2010 John Wiley & Sons A/S.
Figures
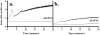
Similar articles
-
Fab fragment glycosylated IgG may play a central role in placental immune evasion.Hum Reprod. 2015 Feb;30(2):380-91. doi: 10.1093/humrep/deu323. Epub 2014 Dec 11. Hum Reprod. 2015. PMID: 25505012 Free PMC article.
-
A flow cytometric comparison of Indo-1 to fluo-3 and Fura Red excited with low power lasers for detecting Ca(2+) flux.J Immunol Methods. 2006 Apr 20;311(1-2):220-5. doi: 10.1016/j.jim.2006.02.005. Epub 2006 Mar 6. J Immunol Methods. 2006. PMID: 16545393
-
Flow cytometric calcium flux assay: evaluation of cytoplasmic calcium kinetics in whole blood leukocytes.J Immunol Methods. 2009 Aug 31;348(1-2):74-82. doi: 10.1016/j.jim.2009.07.002. Epub 2009 Jul 16. J Immunol Methods. 2009. PMID: 19616551
-
Critical growth factors and signalling pathways controlling human trophoblast invasion.Int J Dev Biol. 2010;54(2-3):269-80. doi: 10.1387/ijdb.082769mk. Int J Dev Biol. 2010. PMID: 19876833 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Immunological relationship between the mother and the fetus.Int Rev Immunol. 2002 Nov-Dec;21(6):471-95. doi: 10.1080/08830180215017. Int Rev Immunol. 2002. PMID: 12650238 Review.
Cited by
-
Methylome of fetal and maternal monocytes and macrophages at the feto-maternal interface.Am J Reprod Immunol. 2012 Jul;68(1):8-27. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0897.2012.01108.x. Epub 2012 Mar 2. Am J Reprod Immunol. 2012. PMID: 22385097 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
VIP Promotes Recruitment of Tregs to the Uterine-Placental Interface During the Peri-Implantation Period to Sustain a Tolerogenic Microenvironment.Front Immunol. 2020 Jan 8;10:2907. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2019.02907. eCollection 2019. Front Immunol. 2020. PMID: 31969877 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Luppi P. How immune mechanisms are affected by pregnancy. Vaccine. 2003;21:3352–3357. - PubMed
-
- Aluvihare VR, Kallikourdis M, Betz AG. Tolerance, suppression and the fetal allograft. J Mol Med. 2005;83:88–96. - PubMed
-
- Buyon JP. The effects of pregnancy on autoimmune diseases. J Leukoc Biol. 1998;63:281–287. - PubMed
-
- Confavreux C, Hutchinson M, Hours MM, Cortinovis-Tourniaire P, Moreau T. Rate of pregnancy-related relapse in multiple sclerosis. Pregnancy in Multiple Sclerosis Group. N Engl J Med. 1998;339:285–291. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

