Nongenomic actions of adrenal steroids in the central nervous system
- PMID: 20367759
- PMCID: PMC4676409
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1365-2826.2010.02000.x
Nongenomic actions of adrenal steroids in the central nervous system
Abstract
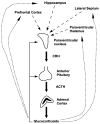
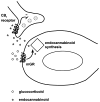
Mineralocorticoids and glucocorticoids are steroid hormones that are released by the adrenal cortex in response to stress and hydromineral imbalance. Historically, adrenocorticosteroid actions are attributed to effects on gene transcription. More recently, however, it has become clear that genome-independent pathways represent an important facet of adrenal steroid actions. These hormones exert nongenomic effects throughout the body, although a significant portion of their actions are specific to the central nervous system. These actions are mediated by a variety of signalling pathways, and lead to physiologically meaningful events in vitro and in vivo. We review the nongenomic effects of adrenal steroids in the central nervous system at the levels of behaviour, neural system activity, individual neurone activity and subcellular signalling activity. A clearer understanding of adrenal steroid activity in the central nervous system will lead to a better ability to treat human disease as well as reduce the side-effects of the steroid treatments already in use.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Multiple actions of steroid hormones--a focus on rapid, nongenomic effects.Pharmacol Rev. 2000 Dec;52(4):513-56. Pharmacol Rev. 2000. PMID: 11121509 Review.
-
Nongenomic steroid actions: fact or fantasy?Vitam Horm. 1999;57:325-73. doi: 10.1016/s0083-6729(08)60647-0. Vitam Horm. 1999. PMID: 10232053 Review.
-
The nature of adrenocorticosteroid activity.Trans Am Acad Ophthalmol Otolaryngol. 1967 Mar-Apr;71(2):243-7. Trans Am Acad Ophthalmol Otolaryngol. 1967. PMID: 4293738 No abstract available.
-
[Steroid therapy and adrenal function].Recenti Prog Med. 2000 Nov;91(11):594-600. Recenti Prog Med. 2000. PMID: 11125954 Review. Italian.
-
Function of the hypothalamo-hypophyseal-adrenal system in mice with ectopic hyperproduction of the agouti protein.Neurosci Behav Physiol. 2005 Feb;35(2):187-91. doi: 10.1007/s11055-005-0068-3. Neurosci Behav Physiol. 2005. PMID: 15779332
Cited by
-
A Comprehensive Overview on Stress Neurobiology: Basic Concepts and Clinical Implications.Front Behav Neurosci. 2018 Jul 3;12:127. doi: 10.3389/fnbeh.2018.00127. eCollection 2018. Front Behav Neurosci. 2018. PMID: 30034327 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Role of corticosterone in altered neurobehavioral responses to acute stress in a model of compromised hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis function.Psychoneuroendocrinology. 2019 Apr;102:248-255. doi: 10.1016/j.psyneuen.2018.12.010. Epub 2018 Dec 11. Psychoneuroendocrinology. 2019. PMID: 30594817 Free PMC article.
-
The molecular physiology of CRH neurons.Front Neuroendocrinol. 2012 Jan;33(1):67-84. doi: 10.1016/j.yfrne.2011.08.002. Epub 2011 Aug 18. Front Neuroendocrinol. 2012. PMID: 21871477 Free PMC article.
-
Stress and neurodevelopmental processes in the emergence of psychosis.Neuroscience. 2013 Sep 26;249:172-91. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2012.12.017. Epub 2013 Jan 5. Neuroscience. 2013. PMID: 23298853 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Synaptocrine signaling: steroid synthesis and action at the synapse.Endocr Rev. 2011 Aug;32(4):532-49. doi: 10.1210/er.2011-0004. Epub 2011 May 26. Endocr Rev. 2011. PMID: 21622487 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Sapolsky RM, Romero LM, Munck AU. How do glucocorticoids influence stress responses? Integrating permissive, suppressive, stimulatory, and preparative actions. Endocr Rev. 2000;21:55–89. - PubMed
-
- Ganong WF, Mulrow PJ. Rate of change in sodium and potassium excretion after injection of aldosterone into the aorta and renal artery of the dog. Am J Physiol. 1958;195:337–342. - PubMed
-
- Klein K, Henk W. Clinical experimental studies on the influence of aldosterone on hemodynamics and blod coagulation. Z Kreislaufforsch. 1963;52:40–53. - PubMed
-
- Moura AM, Worcel M. Direct action of aldosterone on transmembrane 22Na efflux from arterial smooth muscle. Rapid and delayed effects. Hypertension. 1984;6:425–430. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- DK048061/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- MH069725/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- T32 NS007453/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R29 DK048061/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- HL096830/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- F32 DK079710/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK066596/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- DK066596/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- DK79710/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- K99 HL096830/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R00 HL096830/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK048061/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH069725/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- NS007453/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

