Docosahexaenoic acid-enriched fish oil attenuates kidney disease and prolongs median and maximal life span of autoimmune lupus-prone mice
- PMID: 20368275
- PMCID: PMC2952419
- DOI: 10.4049/jimmunol.0903282
Docosahexaenoic acid-enriched fish oil attenuates kidney disease and prolongs median and maximal life span of autoimmune lupus-prone mice
Abstract
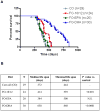
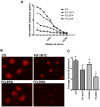
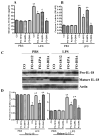
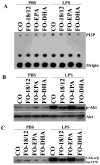
The therapeutic efficacy of individual components of fish oils (FOs) in various human inflammatory diseases still remains unresolved, possibly due to low levels of n-3 fatty acids docosahexaenoic acid (DHA) and eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA) or lower ratio of DHA to EPA. Because FO enriched with DHA (FO-DHA) or EPA (FO-EPA) has become available recently, we investigated their efficacy on survival and inflammatory kidney disease in a well-established animal model of human systemic lupus erythematosus. Results show for the first time that FO-DHA dramatically extends both the median (658 d) and maximal (848 d) life span of (NZB x NZW)F1 (B x W) mice. In contrast, FO-EPA fed mice had a median and maximal life span of approximately 384 and 500 d, respectively. Investigations into possible survival mechanisms revealed that FO-DHA (versus FO-EPA) lowers serum anti-dsDNA Abs, IgG deposition in kidneys, and proteinuria. Further, FO-DHA lowered LPS-mediated increases in serum IL-18 levels and caspase-1-dependent cleavage of pro-IL-18 to mature IL-18 in kidneys. Moreover, FO-DHA suppressed LPS-mediated PI3K, Akt, and NF-kappaB activations in kidney. These data indicate that DHA, but not EPA, is the most potent n-3 fatty acid that suppresses glomerulonephritis and extends life span of systemic lupus erythematosus-prone short-lived B x W mice, possibly via inhibition of IL-18 induction and IL-18-dependent signaling.
Figures
References
-
- Kotzin BL. Systemic lupus erythematosus. Cell. 1996;85:303–306. - PubMed
-
- Rahman A, Isenberg DA. Systemic lupus erythematosus. N Engl J Med. 2008;358:929–939. - PubMed
-
- Helyer BJ, Howie JB. Renal disease associated with positive lupus erythematosus tests in a cross-bred strain of mice. Nature. 1963;197:197. - PubMed
-
- Theofilopoulos AN, Dixon FJ. Murine models of systemic lupus erythematosus. Adv Immunol. 1985;37:269–390. - PubMed
-
- Novick D, Elbirt D, Miller G, Dinarello CA, Rubinstein M, Sthoeger ZM. High circulating levels of free interleukin-18 in patients with active SLE in the presence of elevated levels of interleukin-18 binding protein. J Autoimmun 2009 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

