EKLF directly activates the p21WAF1/CIP1 gene by proximal promoter and novel intronic regulatory regions during erythroid differentiation
- PMID: 20368355
- PMCID: PMC2876526
- DOI: 10.1128/MCB.01016-09
EKLF directly activates the p21WAF1/CIP1 gene by proximal promoter and novel intronic regulatory regions during erythroid differentiation
Abstract
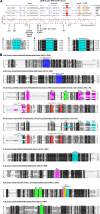
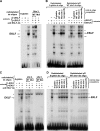
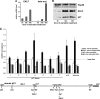
The switch from proliferation to differentiation during the terminal stages of erythropoiesis is a tightly controlled process that relies in part on transcription factor-mediated activation of cell cycle components. EKLF is a key transcription factor that is necessary for the initial establishment of the red cell phenotype. Here, we find that EKLF also plays a role during the subsequent differentiation process, as it induces p21(WAF1/CIP1) expression independent of p53 to regulate the changes in the cell cycle underlying erythroid maturation. EKLF activates p21 not only by directly binding to an EKLF site within a previously characterized GC-rich region in the p21 proximal promoter but also by occupancy at a novel, phylogenetically conserved region that contains consensus CACCC core motifs located downstream from the p21 TATA box. Our findings demonstrate that EKLF, likely in coordination with other transcription factors, directly contributes to the complex set of events that occur at the final erythroid cell divisions and accentuates terminal differentiation directly by activation of CDK inhibitors such as p21.
Figures




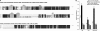
Similar articles
-
Failure of terminal erythroid differentiation in EKLF-deficient mice is associated with cell cycle perturbation and reduced expression of E2F2.Mol Cell Biol. 2008 Dec;28(24):7394-401. doi: 10.1128/MCB.01087-08. Epub 2008 Oct 13. Mol Cell Biol. 2008. PMID: 18852285 Free PMC article.
-
Erythroid Kruppel-like factor regulates the G1 cyclin dependent kinase inhibitor p18INK4c.J Mol Biol. 2007 Jun 1;369(2):313-21. doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2007.02.109. Epub 2007 Mar 20. J Mol Biol. 2007. PMID: 17442339
-
Erythroid Krüppel-like factor directly activates the basic Krüppel-like factor gene in erythroid cells.Mol Cell Biol. 2007 Apr;27(7):2777-90. doi: 10.1128/MCB.01658-06. Epub 2007 Feb 5. Mol Cell Biol. 2007. PMID: 17283065 Free PMC article.
-
KLF1 directly coordinates almost all aspects of terminal erythroid differentiation.IUBMB Life. 2010 Dec;62(12):886-90. doi: 10.1002/iub.404. IUBMB Life. 2010. PMID: 21190291 Review.
-
The multifunctional role of EKLF/KLF1 during erythropoiesis.Blood. 2011 Aug 25;118(8):2044-54. doi: 10.1182/blood-2011-03-331371. Epub 2011 May 25. Blood. 2011. PMID: 21613252 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Severe anemia in the Nan mutant mouse caused by sequence-selective disruption of erythroid Kruppel-like factor.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2010 Aug 24;107(34):15151-6. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1004996107. Epub 2010 Aug 9. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2010. PMID: 20696915 Free PMC article.
-
Erythro-megakaryocytic transcription factors associated with hereditary anemia.Blood. 2014 May 15;123(20):3080-8. doi: 10.1182/blood-2014-01-453167. Epub 2014 Mar 20. Blood. 2014. PMID: 24652993 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Severe anemia caused by dominant mutations in Krüppel-like factor 1 (KLF1).Mutat Res Rev Mutat Res. 2020 Oct-Dec;786:108336. doi: 10.1016/j.mrrev.2020.108336. Epub 2020 Oct 9. Mutat Res Rev Mutat Res. 2020. PMID: 33339573 Free PMC article. Review.
-
EKLF/KLF1, a tissue-restricted integrator of transcriptional control, chromatin remodeling, and lineage determination.Mol Cell Biol. 2013 Jan;33(1):4-13. doi: 10.1128/MCB.01058-12. Epub 2012 Oct 22. Mol Cell Biol. 2013. PMID: 23090966 Free PMC article. Review.
-
KLF1/EKLF expression in acute leukemia is correlated with chromosomal abnormalities.Blood Cells Mol Dis. 2020 Jul;83:102434. doi: 10.1016/j.bcmd.2020.102434. Epub 2020 Apr 13. Blood Cells Mol Dis. 2020. PMID: 32311573 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bao, S., and R. Cagan. 2005. Preferential adhesion mediated by Hibris and Roughest regulates morphogenesis and patterning in the Drosophila eye. Dev. Cell 8:925-935. - PubMed
-
- Bieker, J. J. 2000. EKLF and the development of the erythroid lineage, p. 71-84. In J. D. Light and K. Ravid (ed.), Transcription factors: normal and malignant development of blood cells. Wiley-Liss, New York, NY.
-
- Bieker, J. J. 1996. Isolation, genomic structure, and expression of human erythroid Kruppel-like factor (EKLF). DNA Cell Biol. 15:347-352. - PubMed
-
- Bouilloux, F., G. Juban, N. Cohet, D. Buet, B. Guyot, W. Vainchenker, F. Louache, and F. Morle. 2008. EKLF restricts megakaryocytic differentiation at the benefit of erythrocytic differentiation. Blood 112:576-584. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
