Networking with AKAPs: context-dependent regulation of anchored enzymes
- PMID: 20368369
- PMCID: PMC2895371
- DOI: 10.1124/mi.10.2.6
Networking with AKAPs: context-dependent regulation of anchored enzymes
Abstract
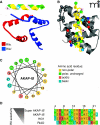
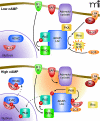
A-Kinase Anchoring Proteins (AKAPs) orchestrate and synchronize cellular events by tethering the cAMP-dependent protein kinase (PKA) and other signaling enzymes to organelles and membranes. The control of kinases and phosphatases that are held in proximity to activators, effectors, and substrates favors the rapid dissemination of information from one cellular location to the next. This article charts the inception of the PKA-anchoring hypothesis, the characterization of AKAPs and their nomenclature, and the physiological roles of context-specific AKAP signaling complexes.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Regulation of neuronal PKA signaling through AKAP targeting dynamics.Eur J Cell Biol. 2006 Jul;85(7):627-33. doi: 10.1016/j.ejcb.2006.01.010. Epub 2006 Feb 28. Eur J Cell Biol. 2006. PMID: 16504338 Review.
-
Single nucleotide polymorphisms alter kinase anchoring and the subcellular targeting of A-kinase anchoring proteins.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2018 Dec 4;115(49):E11465-E11474. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1816614115. Epub 2018 Nov 19. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2018. PMID: 30455320 Free PMC article.
-
The role of A-Kinase anchoring proteins in cAMP-mediated signal transduction pathways.Cell Biochem Biophys. 2004;40(3 Suppl):201-8. doi: 10.1385/cbb:40:3:201. Cell Biochem Biophys. 2004. PMID: 15289655 Review.
-
Cytoplasmic anchoring of cAMP-dependent protein kinase (PKA) by A-kinase anchor proteins (AKAPs) is required for meiotic arrest of porcine full-grown and growing oocytes.Biol Reprod. 2014 Mar 20;90(3):58. doi: 10.1095/biolreprod.113.114736. Print 2014 Mar. Biol Reprod. 2014. PMID: 24501172
-
Pharmacological Interference With Protein-protein Interactions of Akinase Anchoring Proteins as a Strategy for the Treatment of Disease.Curr Drug Targets. 2016;17(10):1147-71. doi: 10.2174/1389450116666150416114247. Curr Drug Targets. 2016. PMID: 25882214 Review.
Cited by
-
PKA-type I selective constrained peptide disruptors of AKAP complexes.ACS Chem Biol. 2015 Jun 19;10(6):1502-10. doi: 10.1021/acschembio.5b00009. Epub 2015 Mar 25. ACS Chem Biol. 2015. PMID: 25765284 Free PMC article.
-
A-kinase Anchoring Protein 79/150 Recruits Protein Kinase C to Phosphorylate Roundabout Receptors.J Biol Chem. 2015 May 29;290(22):14107-19. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M115.637470. Epub 2015 Apr 16. J Biol Chem. 2015. PMID: 25882844 Free PMC article.
-
Spinophilin regulates phosphorylation and interactions of the GluN2B subunit of the N-methyl-d-aspartate receptor.J Neurochem. 2019 Oct;151(2):185-203. doi: 10.1111/jnc.14831. Epub 2019 Aug 2. J Neurochem. 2019. PMID: 31325175 Free PMC article.
-
A phosphodiesterase 2A isoform localized to mitochondria regulates respiration.J Biol Chem. 2011 Sep 2;286(35):30423-30432. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M111.266379. Epub 2011 Jul 1. J Biol Chem. 2011. PMID: 21724846 Free PMC article.
-
A-kinase anchoring proteins: scaffolding proteins in the heart.Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2011 Nov;301(5):H1742-53. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.00569.2011. Epub 2011 Aug 19. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2011. PMID: 21856912 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Sutherland EW, Robison GA. (1966) The Role of Cyclic-3’,5’-AMP in Responses to Catecholamines and Other Hormones. Pharmacol Rev 18:145–161 - PubMed
-
- Bender AT, Beavo JA. (2006) Cyclic Nucleotide Phosphodiesterases: Molecular Regulation to Clinical Use. Pharmacol Rev 58:488–520 - PubMed
-
- Hanoune J, Defer N. (2001) Regulation and Role of Adenylyl Cyclase Isoforms. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol 41:145–174 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
