Low prevalence of fks1 hot spot 1 mutations in a worldwide collection of Candida strains
- PMID: 20368396
- PMCID: PMC2876398
- DOI: 10.1128/AAC.01711-09
Low prevalence of fks1 hot spot 1 mutations in a worldwide collection of Candida strains
Abstract
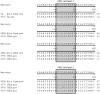
We evaluated the prevalence of fks1 hot spot (HS) 1 mutations among 133 Candida strains from six species displaying various caspofungin MIC values (from < or =0.008 to >8 microg/ml). Only 4 (2.9%) strains displayed FKS1 HS1 amino acid substitutions: 1 C. albicans (F641Y) among 32 isolates tested (3.1%), 1 C. glabrata (S645P) among 34 isolates tested (2.9%), and 2 C. tropicalis (F641S) among 12 isolates tested (16.7%). The 4 isolates displaying FKS1 HS1 alterations showed elevated caspofungin MIC results (1 to >8 microg/ml) but lower anidulafungin and micafungin MIC values (0.12 to 4 microg/ml and 0.25 to 4 microg/ml, respectively) in some instances within the wild-type MIC population, as determined using the epidemiologic cutoff values (ECV). Candida krusei, C. parapsilosis, and C. guilliermondii isolates tested showed no FKS1 HS1 alterations regardless of echinocandin MIC result. We additionally analyzed 8 C. albicans and 7 C. glabrata strains for mutations on other HS regions of fks1 and fks2. Three C. glabrata strains showed alterations on FKS2 HS1 (two S645P and one L644W). In general, strains displaying S645P alteration showed higher echinocandin MIC values than strains harboring other mutations. Overall, Candida spp. strains showing caspofungin MIC values within the ECV did not display fks HS mutations. In contrast, strains showing alterations in this region displayed anidulafungin and/or micafungin MIC values within the wild-type population, suggesting that caspofungin could be the most sensitive agent for detection of these resistance mutations. Furthermore, results from this large, geographically diverse Candida spp. collection demonstrated that fks1 HS1 mutations remain uncommon among isolates with various echinocandin MIC levels.
Figures
References
-
- Baixench, M. T., N. Aoun, M. Desnos-Ollivier, D. Garcia-Hermoso, S. Bretagne, S. Ramires, C. Piketty, and E. Dannaoui. 2007. Acquired resistance to echinocandins in Candida albicans: case report and review. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 59:1076-1083. - PubMed
-
- Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute. 2008. M27-A3. Reference method for broth dilution antifungal susceptibility testing of yeasts. Third edition. Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute, Wayne, PA.
-
- Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute. 2008. M27-S3. Reference method for broth dilution antifungal susceptibility testing of yeasts. 3rd informational supplement. Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute, Wayne, PA.
-
- Desnos-Ollivier, M., S. Bretagne, D. Raoux, D. Hoinard, F. Dromer, and E. Dannaoui. 2008. Mutations in the fks1 gene in Candida albicans, C. tropicalis, and C. krusei correlate with elevated caspofungin MICs uncovered in AM3 medium using the method of the European Committee on Antibiotic Susceptibility Testing. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 52:3092-3098. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Gafter-Gvili, A., L. Vidal, E. Goldberg, L. Leibovici, and M. Paul. 2008. Treatment of invasive candidal infections: systematic review and meta-analysis. Mayo Clin. Proc. 83:1011-1021. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous