Sitagliptin (MK0431) inhibition of dipeptidyl peptidase IV decreases nonobese diabetic mouse CD4+ T-cell migration through incretin-dependent and -independent pathways
- PMID: 20368408
- PMCID: PMC2889774
- DOI: 10.2337/db09-1618
Sitagliptin (MK0431) inhibition of dipeptidyl peptidase IV decreases nonobese diabetic mouse CD4+ T-cell migration through incretin-dependent and -independent pathways
Abstract
Objective: Treatment of NOD mice with the dipeptidyl peptidase-IV (DPP-IV) inhibitor sitagliptin preserved islet transplants through a pathway involving modulation of splenic CD4(+) T-cell migration. In the current study, effects of sitagliptin on migration of additional subsets of CD4(+) T-cells were examined and underlying molecular mechanisms were further defined.
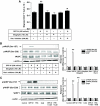
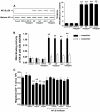
Research design and methods: Effects of sitagliptin on migration of NOD mouse splenic, thymic, and lymph node CD4(+) T-cells were determined. Signaling modules involved in DPP-IV-, Sitagliptin- and incretin-mediated modulation of CD4(+) T-cell migration were studied using Western blot and Rac1 and nuclear factor-kappaB (NF-kappaB) activity assays.
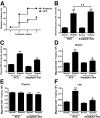
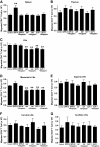
Results: Migration of splenic and lymph node CD4(+) T-cells of diabetic NOD mice was reduced by sitagliptin treatment. In vitro treatment of splenic, but not thymic or lymph node CD4(+) T-cells, from nondiabetic NOD mice with soluble (s) DPP-IV increased migration. Sitagliptin abolished sDPP-IV effects on splenic CD4(+) T-cell migration, whereas incretins decreased migration of lymph node, but not splenic, CD4(+) T-cells. Splenic CD4(+) T-cells demonstrating increased in vitro migration in response to sDPP-IV and lymph node CD4(+) T-cells that were nonresponsive to incretins selectively infiltrated islets of NOD mice, after injection. Sitagliptin decreases migration of splenic CD4(+) T-cells through a pathway involving Rac1/vasodilator-stimulated phosphoprotein, whereas its inhibitory effects on the migration of lymph node CD4(+) T-cells involve incretin-activation of the NF-kappaB pathway.
Conclusions: Benefits of sitagliptin treatment in diabetic NOD mice may be mediated through selective effects on subpopulations of T-cells that are related to autoimmunity.
Figures



References
-
- Brubaker PL, Drucker DJ: Minireview: Glucagon-like peptides regulate cell proliferation and apoptosis in the pancreas, gut, and central nervous system. Endocrinology 2004;145:2653–2659 - PubMed
-
- Yusta B, Baggio LL, Estall JL, Koehler JA, Holland DP, Li H, Pipeleers D, Ling Z, Drucker DJ: GLP-1 receptor activation improves beta cell function and survival following induction of endoplasmic reticulum stress. Cell Metab 2006;4:391–406 - PubMed
-
- Ehses JA, Casilla VR, Doty T, Pospisilik JA, Winter KD, Demuth HU, Pederson RA, McIntosh CH: Glucose-dependent insulinotropic polypeptide promotes beta-(INS-1) cell survival via cyclic adenosine monophosphate-mediated caspase-3 inhibition and regulation of p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase. Endocrinology 2003;144:4433–4445 - PubMed
-
- Kim SJ, Winter K, Nian C, Tsuneoka M, Koda Y, McIntosh CH: Glucose-dependent insulinotropic polypeptide (GIP) stimulation of pancreatic beta-cell survival is dependent upon phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase (PI3K)/protein kinase B (PKB) signaling, inactivation of the forkhead transcription factor Foxo1, and down-regulation of bax expression. J Biol Chem 2005;280:22297–22307 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

