Legionella pneumophila 6S RNA optimizes intracellular multiplication
- PMID: 20368425
- PMCID: PMC2867745
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0911764107
Legionella pneumophila 6S RNA optimizes intracellular multiplication
Abstract
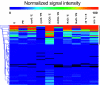
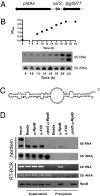
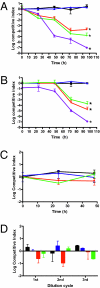
Legionella pneumophila is a Gram-negative opportunistic human pathogen that infects and multiplies in a broad range of phagocytic protozoan and mammalian phagocytes. Based on the observation that small regulatory RNAs (sRNAs) play an important role in controlling virulence-related genes in several pathogenic bacteria, we attempted to identify sRNAs expressed by L. pneumophila. We used computational prediction followed by experimental verification to identify and characterize sRNAs encoded in the L. pneumophila genome. A 50-mer probe microarray was constructed to test the expression of predicted sRNAs in bacteria grown under a variety of conditions. This strategy successfully identified 22 expressed RNAs, out of which 6 were confirmed by northern blot and RACE. One of the identified sRNAs is highly expressed in postexponential phase, and computational prediction of its secondary structure reveals a striking similarity to the structure of 6S RNA, a widely distributed prokaryotic sRNA, known to regulate the activity of sigma(70)-containing RNA polymerase. A 70-mer probe microarray was used to identify genes affected by L. pneumophila 6S RNA in stationary phase. The 6S RNA positively regulates expression of genes encoding type IVB secretion system effectors, stress response genes such as groES and recA, as well as many genes involved in acquisition of nutrients and genes with unknown or hypothetical functions. Deletion of 6S RNA significantly reduced L. pneumophila intracellular multiplication in both protist and mammalian host cells, but had no detectable effect on growth in rich media.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Sequencing illustrates the transcriptional response of Legionella pneumophila during infection and identifies seventy novel small non-coding RNAs.PLoS One. 2011 Mar 3;6(3):e17570. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0017570. PLoS One. 2011. PMID: 21408607 Free PMC article.
-
SigmaS controls multiple pathways associated with intracellular multiplication of Legionella pneumophila.J Bacteriol. 2009 Apr;191(8):2461-73. doi: 10.1128/JB.01578-08. Epub 2009 Feb 13. J Bacteriol. 2009. PMID: 19218380 Free PMC article.
-
The Legionella pneumophila response regulator LqsR promotes host cell interactions as an element of the virulence regulatory network controlled by RpoS and LetA.Cell Microbiol. 2007 Dec;9(12):2903-20. doi: 10.1111/j.1462-5822.2007.01005.x. Epub 2007 Jul 5. Cell Microbiol. 2007. PMID: 17614967
-
Facets of small RNA-mediated regulation in Legionella pneumophila.Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 2013;376:53-80. doi: 10.1007/82_2013_347. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 2013. PMID: 23918178 Review.
-
The perplexing functions and surprising origins of Legionella pneumophila type IV secretion effectors.Cell Microbiol. 2009 Oct;11(10):1435-43. doi: 10.1111/j.1462-5822.2009.01351.x. Epub 2009 Jun 26. Cell Microbiol. 2009. PMID: 19563462 Review.
Cited by
-
Characterization of 6S RNA in the Lyme disease spirochete.Mol Microbiol. 2020 Feb;113(2):399-417. doi: 10.1111/mmi.14427. Epub 2019 Dec 11. Mol Microbiol. 2020. PMID: 31742773 Free PMC article.
-
Global regulation of transcription by a small RNA: a quantitative view.Biophys J. 2014 Mar 4;106(5):1205-14. doi: 10.1016/j.bpj.2014.01.025. Biophys J. 2014. PMID: 24606944 Free PMC article.
-
Bacterial small RNAs in the Genus Rickettsia.BMC Genomics. 2015 Dec 18;16:1075. doi: 10.1186/s12864-015-2293-7. BMC Genomics. 2015. PMID: 26679185 Free PMC article.
-
Virulence phenotypes of Legionella pneumophila associated with noncoding RNA lpr0035.Infect Immun. 2012 Dec;80(12):4143-53. doi: 10.1128/IAI.00598-12. Epub 2012 Sep 10. Infect Immun. 2012. PMID: 22966048 Free PMC article.
-
Bacterial Small RNAs in Mixed Regulatory Networks.Microbiol Spectr. 2018 May;6(3):10.1128/microbiolspec.rwr-0014-2017. doi: 10.1128/microbiolspec.RWR-0014-2017. Microbiol Spectr. 2018. PMID: 29916348 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Fraser DW, et al. Legionnaires’ disease: Description of an epidemic of pneumonia. N Engl J Med. 1977;297:1189–1197. - PubMed
-
- Shin S, Roy CR. Host cell processes that influence the intracellular survival of Legionella pneumophila. Cell Microbiol. 2008;10:1209–1220. - PubMed
-
- Franco IS, Shuman HA, Charpentier X. The perplexing functions and surprising origins of Legionella pneumophila type IV secretion effectors. Cell Microbiol. 2009;11:1435–1443. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

