Human adult vena saphena contains perivascular progenitor cells endowed with clonogenic and proangiogenic potential
- PMID: 20368523
- PMCID: PMC2917746
- DOI: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.109.899252
Human adult vena saphena contains perivascular progenitor cells endowed with clonogenic and proangiogenic potential
Abstract
Background: Clinical trials in ischemic patients showed the safety and benefit of autologous bone marrow progenitor cell transplantation. Non-bone marrow progenitor cells with proangiogenic capacities have been described, yet they remain clinically unexploited owing to their scarcity, difficulty of access, and low ex vivo expansibility. We investigated the presence, antigenic profile, expansion capacity, and proangiogenic potential of progenitor cells from the saphenous vein of patients undergoing coronary artery bypass surgery.
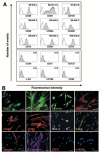
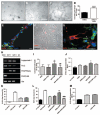
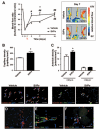
Methods and results: CD34-positive cells, negative for the endothelial marker von Willebrand factor, were localized around adventitial vasa vasorum. After dissection of the vein from surrounding tissues and enzymatic digestion, CD34-positive/CD31-negative cells were isolated by selective culture, immunomagnetic beads, or fluorescence-assisted cell sorting. In the presence of serum, CD34-positive/CD31-negative cells gave rise to a highly proliferative population that expressed pericyte/mesenchymal antigens together with the stem cell marker Sox2 and showed clonogenic and multilineage differentiation capacities. We called this population "saphenous vein-derived progenitor cells" (SVPs). In culture, SVPs integrated into networks formed by endothelial cells and supported angiogenesis through paracrine mechanisms. Reciprocally, endothelial cell-released factors facilitated SVP migration. These interactive responses were inhibited by Tie-2 or platelet-derived growth factor-BB blockade. Intramuscular injection of SVPs in ischemic limbs of immunodeficient mice improved neovascularization and blood flow recovery. At 14 days after transplantation, proliferating SVPs were still detectable in the recipient muscles, where they established N-cadherin-mediated physical contact with the capillary endothelium.
Conclusions: SVPs generated from human vein CD34-positive/CD31-negative progenitor cells might represent a new therapeutic tool for angiogenic therapy in ischemic patients.
Figures




References
-
- Howson KM, Aplin AC, Gelati M, Alessandri G, Parati EA, Nicosia RF. The postnatal rat aorta contains pericyte progenitor cells that form spheroidal colonies in suspension culture. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2005;289:C1396–C1407. - PubMed
-
- Invernici G, Emanueli C, Madeddu P, Cristini S, Gadau S, Benetti A, Ciusani E, Stassi G, Siragusa M, Nicosia R, Peschle C, Fascio U, Colombo A, Rizzuti T, Parati E, Alessandri G. Human fetal aorta contains vascular progenitor cells capable of inducing vasculogenesis, angiogenesis, and myogenesis in vitro and in a murine model of peripheral ischemia. Am J Pathol. 2007;170:1879–1892. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Zengin E, Chalajour F, Gehling UM, Ito WD, Treede H, Lauke H, Weil J, Reichenspurner H, Kilic N, Ergun S. Vascular wall resident progenitor cells: a source for postnatal vasculogenesis. Development. 2006;133:1543–1551. - PubMed
-
- Barcelos LS, Duplaa C, Krankel N, Graiani G, Invernici G, Katare R, Siragusa M, Meloni M, Campesi I, Monica M, Simm A, Campagnolo P, Mangialardi G, Stevanato L, Alessandri G, Emanueli C, Madeddu P. Human CD133+ progenitor cells promote the healing of diabetic ischemic ulcers by paracrine stimulation of angiogenesis and activation of Wnt signaling. Circ Res. 2009;104:1095–1102. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Beltrami AP, Cesselli D, Bergamin N, Marcon P, Rigo S, Puppato E, D'Aurizio F, Verardo R, Piazza S, Pignatelli A, Poz A, Baccarani U, Damiani D, Fanin R, Mariuzzi L, Finato N, Masolini P, Burelli S, Belluzzi O, Schneider C, Beltrami CA. Multipotent cells can be generated in vitro from several adult human organs (heart, liver, and bone marrow) Blood. 2007;110:3438–3446. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

