Polymorphisms of LIG4, BTBD2, HMGA2, and RTEL1 genes involved in the double-strand break repair pathway predict glioblastoma survival
- PMID: 20368557
- PMCID: PMC2881725
- DOI: 10.1200/JCO.2009.26.6213
Polymorphisms of LIG4, BTBD2, HMGA2, and RTEL1 genes involved in the double-strand break repair pathway predict glioblastoma survival
Abstract
Purpose: Glioblastoma (GBM) is the most common and aggressive type of glioma and has the poorest survival. However, a small percentage of patients with GBM survive well beyond the established median. Therefore, identifying the genetic variants that influence this small number of unusually long-term survivors may provide important insight into tumor biology and treatment.
Patients and methods: Among 590 patients with primary GBM, we evaluated associations of survival with the 100 top-ranking glioma susceptibility single nucleotide polymorphisms from our previous genome-wide association study using Cox regression models. We also compared differences in genetic variation between short-term survivors (STS; <or= 12 months) and long-term survivors (LTS; >or= 36 months), and explored classification and regression tree analysis for survival data. We tested results using two independent series totaling 543 GBMs.
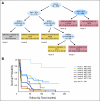
Results: We identified LIG4 rs7325927 and BTBD2 rs11670188 as predictors of STS in GBM and CCDC26 rs10464870 and rs891835, HMGA2 rs1563834, and RTEL1 rs2297440 as predictors of LTS. Further survival tree analysis revealed that patients >or= 50 years old with LIG4 rs7325927 (V) had the worst survival (median survival time, 1.2 years) and exhibited the highest risk of death (hazard ratio, 17.53; 95% CI, 4.27 to 71.97) compared with younger patients with combined RTEL1 rs2297440 (V) and HMGA2 rs1563834 (V) genotypes (median survival time, 7.8 years).
Conclusion: Polymorphisms in the LIG4, BTBD2, HMGA2, and RTEL1 genes, which are involved in the double-strand break repair pathway, are associated with GBM survival.
Conflict of interest statement
Authors' disclosures of potential conflicts of interest and author contributions are found at the end of this article.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Genetic polymorphisms of DNA double-strand break repair pathway genes and glioma susceptibility.BMC Cancer. 2013 May 10;13:234. doi: 10.1186/1471-2407-13-234. BMC Cancer. 2013. PMID: 23663450 Free PMC article.
-
Association between RTEL1, PHLDB1, and TREH Polymorphisms and Glioblastoma Risk: A Case-Control Study.Med Sci Monit. 2015 Jul 9;21:1983-8. doi: 10.12659/MSM.893723. Med Sci Monit. 2015. PMID: 26156397 Free PMC article.
-
Polymorphisms of LIG4 and XRCC4 involved in the NHEJ pathway interact to modify risk of glioma.Hum Mutat. 2008 Mar;29(3):381-9. doi: 10.1002/humu.20645. Hum Mutat. 2008. PMID: 18165945
-
Lack of association between LIG4 gene polymorphisms and the risk of breast cancer: a HuGE review and meta-analysis.Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2012;13(7):3417-22. doi: 10.7314/apjcp.2012.13.7.3417. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2012. PMID: 22994770 Review.
-
The role of the RTEL1 rs2297440 polymorphism in the risk of glioma development: a meta-analysis.Neurol Sci. 2016 Jul;37(7):1023-31. doi: 10.1007/s10072-016-2531-z. Epub 2016 Mar 3. Neurol Sci. 2016. PMID: 26939676 Review.
Cited by
-
From yeast to mammals: recent advances in genetic control of homologous recombination.DNA Repair (Amst). 2012 Oct 1;11(10):781-8. doi: 10.1016/j.dnarep.2012.07.001. Epub 2012 Aug 11. DNA Repair (Amst). 2012. PMID: 22889934 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Combination treatment of TRAIL, DFMO and radiation for malignant glioma cells.J Neurooncol. 2015 Jun;123(2):217-24. doi: 10.1007/s11060-015-1799-9. Epub 2015 May 3. J Neurooncol. 2015. PMID: 25935110
-
Modeling discrete survival time using genomic feature data.Cancer Inform. 2015 Mar 2;14(Suppl 2):37-43. doi: 10.4137/CIN.S17275. eCollection 2015. Cancer Inform. 2015. PMID: 25861216 Free PMC article.
-
HMGA2 Polymorphisms and Hepatoblastoma Susceptibility: A Five-Center Case-Control Study.Pharmgenomics Pers Med. 2020 Feb 11;13:51-57. doi: 10.2147/PGPM.S241100. eCollection 2020. Pharmgenomics Pers Med. 2020. PMID: 32104047 Free PMC article.
-
A comprehensive in silico investigation into the pathogenic SNPs in the RTEL1 gene and their biological consequences.PLoS One. 2024 Sep 6;19(9):e0309713. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0309713. eCollection 2024. PLoS One. 2024. PMID: 39240887 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Stupp R, Mason WP, van den Bent MJ, et al. Radiotherapy plus concomitant and adjuvant temozolomide for glioblastoma. N Engl J Med. 2005;352:987–996. - PubMed
-
- Scott JN, Rewcastle NB, Brasher PM, et al. Which glioblastoma multiforme patient will become a long-term survivor? A population-based study. Ann Neurol. 1999;46:183–188. - PubMed
-
- Curran WJ, Jr, Scott CB, Horton J, et al. Recursive partitioning analysis of prognostic factors in three Radiation Therapy Oncology Group malignant glioma trials. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1993;85:704–710. - PubMed
-
- Lacroix M, Abi-Said D, Fourney DR, et al. A multivariate analysis of 416 patients with glioblastoma multiforme: Prognosis, extent of resection, and survival. J Neurosurg. 2001;95:190–198. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

