Phase III trial of bevacizumab plus interferon alfa versus interferon alfa monotherapy in patients with metastatic renal cell carcinoma: final results of CALGB 90206
- PMID: 20368558
- PMCID: PMC2860433
- DOI: 10.1200/JCO.2009.26.5561
Phase III trial of bevacizumab plus interferon alfa versus interferon alfa monotherapy in patients with metastatic renal cell carcinoma: final results of CALGB 90206
Abstract
Purpose: Bevacizumab is an antibody that binds vascular endothelial growth factor and has activity in metastatic renal cell carcinoma (RCC). Interferon alfa (IFN-alpha) is the historic standard initial treatment for RCC. A prospective, randomized, phase III trial of bevacizumab plus IFN-alpha versus IFN-alpha monotherapy was conducted.
Patients and methods: Patients with previously untreated, metastatic clear cell RCC were randomly assigned to receive either bevacizumab (10 mg/kg intravenously every 2 weeks) plus IFN-alpha (9 million units subcutaneously three times weekly) or the same dose and schedule of IFN-alpha monotherapy in a multicenter phase III trial. The primary end point was overall survival (OS). Secondary end points were progression-free survival (PFS), objective response rate, and safety.
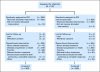
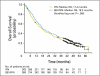
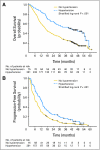
Results: Seven hundred thirty-two patients were enrolled. The median OS time was 18.3 months (95% CI, 16.5 to 22.5 months) for bevacizumab plus IFN-alpha and 17.4 months (95% CI, 14.4 to 20.0 months) for IFN-alpha monotherapy (unstratified log-rank P = .097). Adjusting on stratification factors, the hazard ratio was 0.86 (95% CI, 0.73 to 1.01; stratified log-rank P = .069) favoring bevacizumab plus IFN-alpha. There was significantly more grade 3 to 4 hypertension (HTN), anorexia, fatigue, and proteinuria for bevacizumab plus IFN-alpha. Patients who developed HTN on bevacizumab plus IFN-alpha had a significantly improved PFS and OS versus patients without HTN.
Conclusion: OS favored the bevacizumab plus IFN-alpha arm but did not meet the predefined criteria for significance. HTN may be a biomarker of outcome with bevacizumab plus IFN-alpha.
Conflict of interest statement
Authors' disclosures of potential conflicts of interest and author contributions are found at the end of this article.
Figures

Comment in
-
Have molecularly targeted therapies improved overall survival in renal cell carcinoma?Curr Oncol Rep. 2011 Jun;13(3):153-6. doi: 10.1007/s11912-011-0167-y. Curr Oncol Rep. 2011. PMID: 21455732 No abstract available.
References
-
- Medical Research Council Renal Cancer Collaborators. Interferon-alpha and survival in metastatic renal carcinoma: Early results of a randomised controlled trial. Lancet. 1999;353:14–17. - PubMed
-
- Pyrhönen S, Salminen E, Ruutu M, et al. Prospective randomized trial of interferon alfa-2a plus vinblastine versus vinblastine alone in patients with advanced renal cell cancer. J Clin Oncol. 1999;17:2859–2867. - PubMed
-
- Motzer RJ, Bacik J, Murphy BA, et al. Interferon-alfa as a comparative treatment for clinical trials of new therapies against advanced renal cell carcinoma. J Clin Oncol. 2002;20:289–296. - PubMed
-
- Coppin C, Porzsolt F, Awa A, et al. Immunotherapy for advanced renal cell cancer. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2005;25 CD001425. - PubMed
-
- Negrier S, Escudier B, Lasset C, et al. Recombinant human interleukin-2, recombinant human interferon alfa-2a, or both in metastatic renal-cell carcinoma: Groupe Francais d'Immunotherapie. N Engl J Med. 1998;338:1272–1278. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- U10 CA033601/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA60138/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA45808/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA077440/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA77440/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA041287/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA77202/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA47642/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA047642/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA31946/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA14985/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA33601/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA41287/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA077202/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA045808/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA031946/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

