Fine mapping of ZNF804A and genome-wide significant evidence for its involvement in schizophrenia and bipolar disorder
- PMID: 20368704
- PMCID: PMC3918934
- DOI: 10.1038/mp.2010.36
Fine mapping of ZNF804A and genome-wide significant evidence for its involvement in schizophrenia and bipolar disorder
Abstract
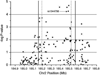
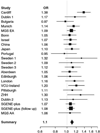
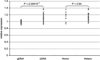
A recent genome-wide association study (GWAS) reported evidence for association between rs1344706 within ZNF804A (encoding zinc-finger protein 804A) and schizophrenia (P=1.61 × 10(-7)), and stronger evidence when the phenotype was broadened to include bipolar disorder (P=9.96 × 10(-9)). In this study we provide additional evidence for association through meta-analysis of a larger data set (schizophrenia/schizoaffective disorder N=18 945, schizophrenia plus bipolar disorder N=21 274 and controls N=38 675). We also sought to better localize the association signal using a combination of de novo polymorphism discovery in exons, pooled de novo polymorphism discovery spanning the genomic sequence of the locus and high-density linkage disequilibrium (LD) mapping. The meta-analysis provided evidence for association between rs1344706 that surpasses widely accepted benchmarks of significance by several orders of magnitude for both schizophrenia (P=2.5 × 10(-11), odds ratio (OR) 1.10, 95% confidence interval 1.07-1.14) and schizophrenia and bipolar disorder combined (P=4.1 × 10(-13), OR 1.11, 95% confidence interval 1.07-1.14). After de novo polymorphism discovery and detailed association analysis, rs1344706 remained the most strongly associated marker in the gene. The allelic association at the ZNF804A locus is now one of the most compelling in schizophrenia to date, and supports the accumulating data suggesting overlapping genetic risk between schizophrenia and bipolar disorder.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Cardno AG, Gottesman II. Twin studies of schizophrenia: from bow-and arrow concordances to star wars Mx and functional genomics (review) Am J Med Genet. 2000;97:12–17. - PubMed
-
- Sullivan PF, Kendler KS, Neale MC. Schizophrenia as a complex trait: evidence from a meta-analysis of twin studies. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 2003;60:1187–1192. - PubMed
-
- Williams HJ, Owen MJ, O'Donovan MC. Schizophrenia genetics: new insights from new approaches. Br Med Bull. 2009;91:61–74. - PubMed
-
- O’Donovan MC, Craddock N, Norton N, Williams H, Peirce T, Moskvina V, et al. Identification of novel schizophrenia loci by genome-wide association and follow-up. Nat Genet. 2008;40:1053–1055. - PubMed

