The HSP70 molecular chaperone is not beneficial in a mouse model of alpha-synucleinopathy
- PMID: 20368804
- PMCID: PMC2848858
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0010014
The HSP70 molecular chaperone is not beneficial in a mouse model of alpha-synucleinopathy
Abstract
Background: Aggregation and misfolded alpha-synuclein is thought to be central in the pathogenesis of Parkinson's disease (PD). Heat-shock proteins (HSPs) that are involved in refolding and degradation processes could lower the aggregate load of alpha-synuclein and thus be beneficial in alpha-synucleinopathies.
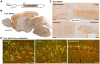
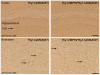
Methodology/principal findings: We co-overexpressed human A53T point-mutated alpha-synuclein and human HSP70 in mice, both under the control of Thy1 regulatory sequences. Behavior read-outs showed no beneficial effect of HSP70 expression in mice. In contrast, motor coordination, grip strength and weight were even worse in the alpha-synucleinopathy model in the presence of HSP70 overexpression. Biochemical analyses revealed no differences in alpha-synuclein oligomers/aggregates, truncations and phosphorylation levels and alpha-synuclein localization was unchanged in immunostainings.
Conclusion/significance: Overexpressing HSP70 in a mouse model of alpha-synucleinopathy did not lower the toxic load of alpha-synuclein species and had no beneficial effect on alpha-synuclein-related motor deficits.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
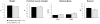
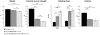

Similar articles
-
Intracranial administration of alpha-synuclein fibrils in A30P-synuclein transgenic mice causes robust synucleinopathy and microglial induction.Neurobiol Aging. 2021 Oct;106:12-25. doi: 10.1016/j.neurobiolaging.2021.05.012. Epub 2021 Jul 3. Neurobiol Aging. 2021. PMID: 34225000
-
Stable alpha-synuclein oligomers strongly inhibit chaperone activity of the Hsp70 system by weak interactions with J-domain co-chaperones.J Biol Chem. 2010 Dec 3;285(49):38173-82. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M110.127753. Epub 2010 Sep 16. J Biol Chem. 2010. PMID: 20847048 Free PMC article.
-
A single amino acid substitution differentiates Hsp70-dependent effects on alpha-synuclein degradation and toxicity.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2004 Dec 3;325(1):367-73. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2004.10.037. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2004. PMID: 15522241
-
Applying chaperones to protein-misfolding disorders: molecular chaperones against α-synuclein in Parkinson's disease.Int J Biol Macromol. 2013 Sep;60:196-205. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2013.05.032. Epub 2013 Jun 5. Int J Biol Macromol. 2013. PMID: 23748003 Review.
-
Parkinson's disease and alpha synuclein: is Parkinson's disease a prion-like disorder?Mov Disord. 2013 Jan;28(1):31-40. doi: 10.1002/mds.25373. Mov Disord. 2013. PMID: 23390095 Review.
Cited by
-
Opportunities and challenges for molecular chaperone modulation to treat protein-conformational brain diseases.Neurotherapeutics. 2013 Jul;10(3):416-28. doi: 10.1007/s13311-013-0186-5. Neurotherapeutics. 2013. PMID: 23536253 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Molecular chaperones and neuronal proteostasis.Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2015 Apr;40:142-52. doi: 10.1016/j.semcdb.2015.03.003. Epub 2015 Mar 12. Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2015. PMID: 25770416 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Challenging Proteostasis: Role of the Chaperone Network to Control Aggregation-Prone Proteins in Human Disease.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2020;1243:53-68. doi: 10.1007/978-3-030-40204-4_4. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2020. PMID: 32297211 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Heat shock protein 70 reduces α-synuclein-induced predegenerative neuronal dystrophy in the α-synuclein viral gene transfer rat model of Parkinson's disease.CNS Neurosci Ther. 2014 Jan;20(1):50-8. doi: 10.1111/cns.12200. Epub 2013 Nov 27. CNS Neurosci Ther. 2014. PMID: 24279716 Free PMC article.
-
Fluc-EGFP reporter mice reveal differential alterations of neuronal proteostasis in aging and disease.EMBO J. 2021 Oct 1;40(19):e107260. doi: 10.15252/embj.2020107260. Epub 2021 Aug 19. EMBO J. 2021. PMID: 34410010 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Singleton AB, Farrer M, Johnson J, Singleton A, Hague S, et al. alpha-Synuclein locus triplication causes Parkinson's disease. Science. 2003;302:841. - PubMed
-
- Polymeropoulos MH, Lavedan C, Leroy E, Ide SE, Dehejia A, et al. Mutation in the alpha-synuclein gene identified in families with Parkinson's disease. Science. 1997;276:2045–2047. - PubMed
-
- Kruger R, Kuhn W, Muller T, Woitalla D, Graeber M, et al. Ala30Pro mutation in the gene encoding alpha-synuclein in Parkinson's disease. Nat Genet. 1998;18:106–108. - PubMed
-
- Zarranz JJ, Alegre J, Gomez-Esteban JC, Lezcano E, Ros R, et al. The new mutation, E46K, of alpha-synuclein causes Parkinson and Lewy body dementia. Ann Neurol. 2004;55:164–173. - PubMed
-
- Douglas MR, Lewthwaite AJ, Nicholl DJ. Genetics of Parkinson's disease and parkinsonism. Expert Rev Neurother. 2007;7:657–666. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

