Enhanced beetle luciferase for high-resolution bioluminescence imaging
- PMID: 20368807
- PMCID: PMC2848861
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0010011
Enhanced beetle luciferase for high-resolution bioluminescence imaging
Abstract
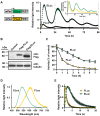
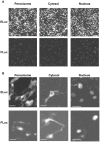
We developed an enhanced green-emitting luciferase (ELuc) to be used as a bioluminescence imaging (BLI) probe. ELuc exhibits a light signal in mammalian cells that is over 10-fold stronger than that of the firefly luciferase (FLuc), which is the most widely used luciferase reporter gene. We showed that ELuc produces a strong light signal in primary cells and tissues and that it enables the visualization of gene expression with high temporal resolution at the single-cell level. Moreover, we successfully imaged the nucleocytoplasmic shuttling of importin alpha by fusing ELuc at the intracellular level. These results demonstrate that the use of ELuc allows a BLI spatiotemporal resolution far greater than that provided by FLuc.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures


References
-
- Wilson T, Hastings JW. Bioluminescence. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol. 1998;14:197–230. - PubMed
-
- Greer LF, Szalay AA. Imaging of light emission from the expression of luciferases in living cells and organisms: a review. Luminescence. 2002;17:43–74. - PubMed
-
- Welsh DK, Kay SA. Bioluminescence imaging in living organisms. Curr Opin Biotechnol. 2005;16:73–78. - PubMed
-
- Roda A, Guardigli M, Michelini E, Mirasoli M. Bioluminescence in analytical chemistry and in vivo imaging. Trends Anal Chem. 2009;28:307–322.
-
- Viviani VR, Silva AC, Perez GL, Santelli RV, Bechara EJ, et al. Cloning and molecular characterization of the cDNA for the Brazilian larval click-beetle Pyrearinus termitilluminans luciferase. Photochem Photobiol. 1999;70:254–260. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

