Incipient balancing selection through adaptive loss of aquaporins in natural Saccharomyces cerevisiae populations
- PMID: 20369021
- PMCID: PMC2848549
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1000893
Incipient balancing selection through adaptive loss of aquaporins in natural Saccharomyces cerevisiae populations
Abstract
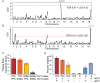
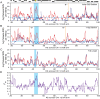
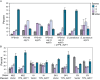
A major goal in evolutionary biology is to understand how adaptive evolution has influenced natural variation, but identifying loci subject to positive selection has been a challenge. Here we present the adaptive loss of a pair of paralogous genes in specific Saccharomyces cerevisiae subpopulations. We mapped natural variation in freeze-thaw tolerance to two water transporters, AQY1 and AQY2, previously implicated in freeze-thaw survival. However, whereas freeze-thaw-tolerant strains harbor functional aquaporin genes, the set of sensitive strains lost aquaporin function at least 6 independent times. Several genomic signatures at AQY1 and/or AQY2 reveal low variation surrounding these loci within strains of the same haplotype, but high variation between strain groups. This is consistent with recent adaptive loss of aquaporins in subgroups of strains, leading to incipient balancing selection. We show that, although aquaporins are critical for surviving freeze-thaw stress, loss of both genes provides a major fitness advantage on high-sugar substrates common to many strains' natural niche. Strikingly, strains with non-functional alleles have also lost the ancestral requirement for aquaporins during spore formation. Thus, the antagonistic effect of aquaporin function-providing an advantage in freeze-thaw tolerance but a fitness defect for growth in high-sugar environments-contributes to the maintenance of both functional and nonfunctional alleles in S. cerevisiae. This work also shows that gene loss through multiple missense and nonsense mutations, hallmarks of pseudogenization presumed to emerge after loss of constraint, can arise through positive selection.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures

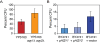
Similar articles
-
Functional relevance of water and glycerol channels in Saccharomyces cerevisiae.FEMS Microbiol Lett. 2017 May 1;364(9). doi: 10.1093/femsle/fnx080. FEMS Microbiol Lett. 2017. PMID: 28430948 Review.
-
Aquaporin-mediated improvement of freeze tolerance of Saccharomyces cerevisiae is restricted to rapid freezing conditions.Appl Environ Microbiol. 2004 Jun;70(6):3377-82. doi: 10.1128/AEM.70.6.3377-3382.2004. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2004. PMID: 15184134 Free PMC article.
-
Aquaporin expression correlates with freeze tolerance in baker's yeast, and overexpression improves freeze tolerance in industrial strains.Appl Environ Microbiol. 2002 Dec;68(12):5981-9. doi: 10.1128/AEM.68.12.5981-5989.2002. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2002. PMID: 12450819 Free PMC article.
-
Polymorphism of Saccharomyces cerevisiae aquaporins.Yeast. 2000 Jul;16(10):897-903. doi: 10.1002/1097-0061(200007)16:10<897::AID-YEA583>3.0.CO;2-T. Yeast. 2000. PMID: 10870101
-
Water Transport in Yeasts.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2016;892:107-124. doi: 10.1007/978-3-319-25304-6_5. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2016. PMID: 26721272 Review.
Cited by
-
The complex genetic and molecular basis of a model quantitative trait.Mol Biol Cell. 2016 Jan 1;27(1):209-18. doi: 10.1091/mbc.E15-06-0408. Epub 2015 Oct 28. Mol Biol Cell. 2016. PMID: 26510497 Free PMC article.
-
Inferring Rates and Length-Distributions of Indels Using Approximate Bayesian Computation.Genome Biol Evol. 2017 May 1;9(5):1280-1294. doi: 10.1093/gbe/evx084. Genome Biol Evol. 2017. PMID: 28453624 Free PMC article.
-
Improved vectors for retron-mediated CRISPR-Cas9 genome editing in Saccharomyces cerevisiae.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2024 Aug 7:2024.08.06.606807. doi: 10.1101/2024.08.06.606807. bioRxiv. 2024. Update in: G3 (Bethesda). 2025 Aug 04:jkaf175. doi: 10.1093/g3journal/jkaf175. PMID: 39149293 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
-
Dynamic large-scale chromosomal rearrangements fuel rapid adaptation in yeast populations.PLoS Genet. 2013;9(1):e1003232. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1003232. Epub 2013 Jan 24. PLoS Genet. 2013. PMID: 23358723 Free PMC article.
-
Adaptation and Phenotypic Diversification in Arabidopsis through Loss-of-Function Mutations in Protein-Coding Genes.Plant Cell. 2019 May;31(5):1012-1025. doi: 10.1105/tpc.18.00791. Epub 2019 Mar 18. Plant Cell. 2019. PMID: 30886128 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Mitchell-Olds T, Willis JH, Goldstein DB. Which evolutionary processes influence natural genetic variation for phenotypic traits? Nat Rev Genet. 2007;8:845–856. - PubMed
-
- Clark AG, Glanowski S, Nielsen R, Thomas PD, Kejariwal A, et al. Inferring nonneutral evolution from human-chimp-mouse orthologous gene trios. Science. 2003;302:1960–1963. - PubMed
-
- Nielsen R, Bustamante C, Clark AG, Glanowski S, Sackton TB, et al. A scan for positively selected genes in the genomes of humans and chimpanzees. PLoS Biol. 2005;3:e170. doi: 10.1371/journal.pbio.0030170. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Sabeti PC, Reich DE, Higgins JM, Levine HZ, Richter DJ, et al. Detecting recent positive selection in the human genome from haplotype structure. Nature. 2002;419:832–837. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

