Gelsolin restores A beta-induced alterations in choroid plexus epithelium
- PMID: 20369065
- PMCID: PMC2847388
- DOI: 10.1155/2010/805405
Gelsolin restores A beta-induced alterations in choroid plexus epithelium
Retraction in
-
Retracted: Gelsolin Restores Aβ-Induced Alterations in Choroid Plexus Epithelium.Biomed Res Int. 2021 Apr 14;2021:9815368. doi: 10.1155/2021/9815368. eCollection 2021. Biomed Res Int. 2021. PMID: 33997047 Free PMC article.
Abstract
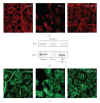
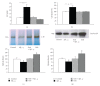
Histologically, Alzheimer's disease (AD) is characterized by senile plaques and cerebrovascular amyloid deposits. In previous studies we demonstrated that in AD patients, amyloid-beta (A beta) peptide also accumulates in choroid plexus, and that this process is associated with mitochondrial dysfunction and epithelial cell death. However, the molecular mechanisms underlying A beta accumulation at the choroid plexus epithelium remain unclear. A beta clearance, from the brain to the blood, involves A beta carrier proteins that bind to megalin, including gelsolin, a protein produced specifically by the choroid plexus epithelial cells. In this study, we show that treatment with gelsolin reduces A beta-induced cytoskeletal disruption of blood-cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) barrier at the choroid plexus. Additionally, our results demonstrate that gelsolin plays an important role in decreasing A beta-induced cytotoxicity by inhibiting nitric oxide production and apoptotic mitochondrial changes. Taken together, these findings make gelsolin an appealing tool for the prophylactic treatment of AD.
Figures

References
-
- Selkoe DJ. The deposition of amyloid proteins in the aging mammalian brain: implications for Alzheimer’s disease. Annals of Medicine. 1989;21(2):73–76. - PubMed
-
- Selkoe DJ. Toward a comprehensive theory for Alzheimer’s disease. Hypothesis: Alzheimer’s disease is caused by the cerebral accumulation and cytotoxicity of amyloid β-protein. Annals of the New York Academy of Sciences. 2000;924:17–25. - PubMed
-
- Glabe C. Intracellular mechanisms of amyloid accumulation and pathogenesis in Alzheimer’s disease. Journal of Molecular Neuroscience. 2001;17(2):137–145. - PubMed
-
- Dietrich MO, Spuch C, Antequera D, et al. Megalin mediates the transport of leptin across the blood-CSF barrier. Neurobiology of Aging. 2008;29(6):902–912. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

