Effect of 2, 5-substituents on the stability of cyclic nitrone superoxide spin adducts: A density functional theory approach
- PMID: 20370568
- PMCID: PMC3074479
- DOI: 10.3109/10715761003758130
Effect of 2, 5-substituents on the stability of cyclic nitrone superoxide spin adducts: A density functional theory approach
Abstract
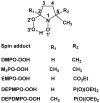
In the present study, five cyclic nitrone superoxide spin adducts, i.e. DMPO-OOH, M(3)PO-OOH, EMPO-OOH, DEPMPO-OOH and DEPDMPO-OOH, were chosen as model compounds to investigate the effect of 2,5-subsitituents on their stability, through structural analysis and decay thermodynamics using density functional theory (DFT) calculations. Analysis of the optimized geometries reveals that none of the previously proposed stabilizing factors, including intramolecular H-bonds, intramolecular non-bonding interactions, bulky steric protection nor the C(2)-N(1) bond distance can be used to clearly explain the effect of 2,5-substituents on the stability of the spin adducts. Subsequent study found that spin densities on the nitroxyl nitrogen and oxygen are well correlated with the half-lives of the spin adducts and consequently are the proper parameters to characterize the effect of 2,5-substituents on their stability. Examination of the decomposition thermodynamics further supports the effect of the substituents on the persistence of cyclic nitrone superoxide spin adducts.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Effect of the phosphoryl substituent in the linear nitrone on the spin trapping of superoxide radical and the stability of the superoxide adduct: combined experimental and theoretical studies.J Org Chem. 2006 Sep 29;71(20):7753-62. doi: 10.1021/jo061204m. J Org Chem. 2006. PMID: 16995683
-
Synthesis and characterization of EMPO-derived 5,5-disubstituted 1-pyrroline N-oxides as spin traps forming exceptionally stable superoxide spin adducts.Biol Chem. 2003 Mar;384(3):493-500. doi: 10.1515/BC.2003.056. Biol Chem. 2003. PMID: 12715901
-
Characterization of the high-resolution ESR spectra of superoxide radical adducts of 5-(diethoxyphosphoryl)-5-methyl-1-pyrroline N-oxide (DEPMPO) and 5,5-dimethyl-1-pyrroline N-oxide (DMPO). Analysis of conformational exchange.Free Radic Res. 2005 Aug;39(8):825-36. doi: 10.1080/10715760500155688. Free Radic Res. 2005. PMID: 16036362
-
Use of spin traps to detect superoxide production in living cells by electron paramagnetic resonance (EPR) spectroscopy.Methods. 2016 Oct 15;109:31-43. doi: 10.1016/j.ymeth.2016.05.001. Epub 2016 May 6. Methods. 2016. PMID: 27163864 Review.
-
Using anti-5,5-dimethyl-1-pyrroline N-oxide (anti-DMPO) to detect protein radicals in time and space with immuno-spin trapping.Free Radic Biol Med. 2004 May 15;36(10):1214-23. doi: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2004.02.077. Free Radic Biol Med. 2004. PMID: 15110386 Review.
References
-
- Bonnett R, Clark VM, Giddy A, Todd A. J Chem Soc. 1959:2087.
- Buettner GR, Oberley LW. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1978;808:235.
- Haire DL, Hilborn JW, Janzen EG. J Org Chem. 1986;51:4298.
-
- Finkelstein E, Rosen GM, Rauckman EJ. Mol Pharmacol. 1982;21:262. - PubMed
- Yamazaki I, Piette LH, Grover TA. J Biol Chem. 1990;265:652. - PubMed
- Villamena FA, Zweier JL. J Chem Soc, Perkin Trans 2. 2002;2:1340.
- Keszler A, Kalyanaraman B, Hogg N. Free Radical Biol Med. 2003;35:1149. - PubMed
- Lauricella R, Allouch A, Roubaud V, Bouteiller JC, Tuccio B. Org Biomol Chem. 2004;2:1304. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
