Prolyl oligopeptidase is inhibited in relapsing-remitting multiple sclerosis
- PMID: 20370893
- PMCID: PMC2864237
- DOI: 10.1186/1742-2094-7-23
Prolyl oligopeptidase is inhibited in relapsing-remitting multiple sclerosis
Abstract
Background: Multiple sclerosis (MS) is a complex, inflammatory and neurodegenerative disease of the central nervous system leading to long-term disability. Recent studies indicate a close association between inflammation and neurodegeneration in all lesions and disease stages of MS. Prolyl oligopeptidase (POP) is a proline-specific serine protease that cleaves several neuroactive peptides. This peptidase has been implicated in neurodegeneration, as well as in the modulation of the inflammatory response.
Methods: We examined plasma POP and the levels of an endogenous POP inhibitor from relapsing remitting MS patients and compared these with healthy controls, by monitoring the fluorescent changes due to standard fluorescently labelled substrate cleavage. We analysed the data in relationship to patient age and disease disability status.
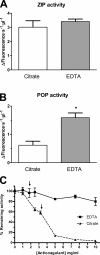
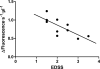
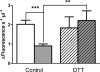
Results: We observed a significant decrease in POP activity in plasma of relapsing remitting MS patients relative to healthy controls, coupled with an increase of POP endogenous inhibitor. The POP activity was also correlated with patient age and disability status. The lowered POP activity from plasma of MS patients could be rescued by reductants
Conclusions: The decrease in circulating POP activity measured in MS is reverted by reductants. This suggests that POP inactivation in MS might be a result of the oxidative conditions prevailing in the plasma of the diseased patients. Plasma levels of POP activity as well as those of their endogenous inhibitor are suggested as biomarkers of inflammation and oxidative stress in MS.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Alteration of prolyl oligopeptidase and activated α-2-macroglobulin in multiple sclerosis subtypes and in the clinically isolated syndrome.Biochem Pharmacol. 2013 Jun 15;85(12):1783-94. doi: 10.1016/j.bcp.2013.04.018. Epub 2013 Apr 30. Biochem Pharmacol. 2013. PMID: 23643808
-
Prolyl oligopeptidase induces angiogenesis both in vitro and in vivo in a novel regulatory manner.Br J Pharmacol. 2011 Aug;163(8):1666-78. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.2010.01146.x. Br J Pharmacol. 2011. PMID: 21133893 Free PMC article.
-
Prolyl oligopeptidase and its role in the organism: attention to the most promising and clinically relevant inhibitors.Future Med Chem. 2017 Jun;9(10):1015-1038. doi: 10.4155/fmc-2017-0030. Epub 2017 Jun 20. Future Med Chem. 2017. PMID: 28632451 Review.
-
The biological role of prolyl oligopeptidase and the procognitive potential of its peptidic inhibitors from food proteins.Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr. 2024;64(19):6567-6580. doi: 10.1080/10408398.2023.2170973. Epub 2023 Feb 16. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr. 2024. PMID: 36798052 Review.
-
Issues about the physiological functions of prolyl oligopeptidase based on its discordant spatial association with substrates and inconsistencies among mRNA, protein levels, and enzymatic activity.J Histochem Cytochem. 2009 Sep;57(9):831-48. doi: 10.1369/jhc.2009.953711. Epub 2009 May 26. J Histochem Cytochem. 2009. PMID: 19687473 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
N-acetyl-seryl-aspartyl-lysyl-proline is a valuable endogenous antifibrotic peptide for kidney fibrosis in diabetes: An update and translational aspects.J Diabetes Investig. 2020 May;11(3):516-526. doi: 10.1111/jdi.13219. Epub 2020 Mar 11. J Diabetes Investig. 2020. PMID: 31997585 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mechanism of Action of Prolyl Oligopeptidase (PREP) in Degenerative Brain Diseases: Has Peptidase Activity Only a Modulatory Role on the Interactions of PREP with Proteins?Front Aging Neurosci. 2017 Feb 14;9:27. doi: 10.3389/fnagi.2017.00027. eCollection 2017. Front Aging Neurosci. 2017. PMID: 28261087 Free PMC article.
-
Structural analysis of prolyl oligopeptidases using molecular docking and dynamics: insights into conformational changes and ligand binding.PLoS One. 2011;6(11):e26251. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0026251. Epub 2011 Nov 23. PLoS One. 2011. PMID: 22132071 Free PMC article.
-
Post-Proline Cleaving Enzymes (PPCEs): Classification, Structure, Molecular Properties, and Applications.Plants (Basel). 2022 May 18;11(10):1330. doi: 10.3390/plants11101330. Plants (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35631755 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The expression levels of prolyl oligopeptidase responds not only to neuroinflammation but also to systemic inflammation upon liver failure in rat models and cirrhotic patients.J Neuroinflammation. 2015 Sep 30;12:183. doi: 10.1186/s12974-015-0404-7. J Neuroinflammation. 2015. PMID: 26420028 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Myöhänen TT, García-Horsman JA, Tenorio-Laranga J, Männistö PT. Issues about the physiological functions of prolyl oligopeptidase based on its discordant spatial association with substrates and inconsistencies among mRNA, protein levels, and enzymatic activity. J Histochem Cytochem. 2009;57:831–848. doi: 10.1369/jhc.2009.953711. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

