The urate-lowering efficacy and safety of febuxostat in the treatment of the hyperuricemia of gout: the CONFIRMS trial
- PMID: 20370912
- PMCID: PMC2888216
- DOI: 10.1186/ar2978
The urate-lowering efficacy and safety of febuxostat in the treatment of the hyperuricemia of gout: the CONFIRMS trial
Abstract
Introduction: The purpose of this study was to compare urate-lowering (UL) efficacy and safety of daily febuxostat and allopurinol in subjects with gout and serum urate (sUA) > or = 8.0 mg/dL in a six-month trial.
Methods: Subjects (n = 2,269) were randomized to febuxostat 40 mg or 80 mg, or allopurinol 300 mg (200 mg in moderate renal impairment). Endpoints included the proportion of all subjects with sUA <6.0 mg/dL and the proportion of subjects with mild/moderate renal impairment and sUA <6.0 mg/dL. Safety assessments included blinded adjudication of each cardiovascular (CV) adverse event (AE) and death.
Results: Comorbidities included: renal impairment (65%); obesity (64%); hyperlipidemia (42%); and hypertension (53%). In febuxostat 40 mg, febuxostat 80 mg, and allopurinol groups, primary endpoint was achieved in 45%, 67%, and 42%, respectively. Febuxostat 40 mg UL was statistically non-inferior to allopurinol, but febuxostat 80 mg was superior to both (P < 0.001). Achievement of target sUA in subjects with renal impairment was also superior with febuxostat 80 mg (72%; P < 0.001) compared with febuxostat 40 mg (50%) or allopurinol (42%), but febuxostat 40 mg showed greater efficacy than allopurinol (P = 0.021). Rates of AEs did not differ across treatment groups. Adjudicated (APTC) CV event rates were 0.0% for febuxostat 40 mg and 0.4% for both febuxostat 80 mg and allopurinol. One death occurred in each febuxostat group and three in the allopurinol group.
Conclusions: Urate-lowering efficacy of febuxostat 80 mg exceeded that of febuxostat 40 mg and allopurinol (300/200 mg), which were comparable. In subjects with mild/moderate renal impairment, both febuxostat doses were more efficacious than allopurinol and equally safe. At the doses tested, safety of febuxostat and allopurinol was comparable.
Clinical trial registration: NCT00430248.
Figures
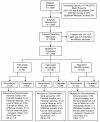
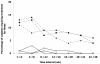
Comment in
-
Advances in gout: some answers, more questions.Arthritis Res Ther. 2010;12(5):136. doi: 10.1186/ar3110. Epub 2010 Sep 24. Arthritis Res Ther. 2010. PMID: 20959031 Free PMC article.
Similar articles
-
Women with gout: efficacy and safety of urate-lowering with febuxostat and allopurinol.Arthritis Care Res (Hoboken). 2012 Feb;64(2):256-61. doi: 10.1002/acr.20680. Arthritis Care Res (Hoboken). 2012. PMID: 22052584 Clinical Trial.
-
The efficacy and safety of febuxostat for urate lowering in gout patients ≥65 years of age.BMC Geriatr. 2012 Mar 21;12:11. doi: 10.1186/1471-2318-12-11. BMC Geriatr. 2012. PMID: 22436129 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Effects of febuxostat versus allopurinol and placebo in reducing serum urate in subjects with hyperuricemia and gout: a 28-week, phase III, randomized, double-blind, parallel-group trial.Arthritis Rheum. 2008 Nov 15;59(11):1540-8. doi: 10.1002/art.24209. Arthritis Rheum. 2008. PMID: 18975369 Clinical Trial.
-
Efficacy and tolerability of febuxostat in hyperuricemic patients with or without gout: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Clin Ther. 2013 Feb;35(2):180-9. doi: 10.1016/j.clinthera.2012.12.011. Epub 2013 Jan 16. Clin Ther. 2013. PMID: 23332451
-
Febuxostat: a selective xanthine-oxidase/xanthine-dehydrogenase inhibitor for the management of hyperuricemia in adults with gout.Clin Ther. 2009 Nov;31(11):2503-18. doi: 10.1016/j.clinthera.2009.11.033. Clin Ther. 2009. PMID: 20109996 Review.
Cited by
-
Comparison of Gout Flares With the Initiation of Treat-to-Target Allopurinol and Febuxostat: A Post-Hoc Analysis of a Randomized Multicenter Trial.Arthritis Rheumatol. 2024 Oct;76(10):1552-1559. doi: 10.1002/art.42927. Epub 2024 Jul 15. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2024. PMID: 38925627 Clinical Trial.
-
A Genome-Wide Association Study of Oxypurinol Concentrations in Patients Treated with Allopurinol.J Pers Med. 2024 Jun 18;14(6):649. doi: 10.3390/jpm14060649. J Pers Med. 2024. PMID: 38929870 Free PMC article.
-
Latest evidence on gout management: what the clinician needs to know.Ther Adv Chronic Dis. 2012 Nov;3(6):271-86. doi: 10.1177/2040622312462056. Ther Adv Chronic Dis. 2012. PMID: 23342241 Free PMC article.
-
Effectiveness and safety of different doses of febuxostat compared with allopurinol in the treatment of hyperuricemia: a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials.BMC Pharmacol Toxicol. 2023 Dec 14;24(1):79. doi: 10.1186/s40360-023-00723-5. BMC Pharmacol Toxicol. 2023. PMID: 38098046 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of febuxostat on renal function in patients with chronic kidney disease: A systematic review and meta-analysis.Medicine (Baltimore). 2019 Jul;98(29):e16311. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000016311. Medicine (Baltimore). 2019. PMID: 31335677 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Arromdee E, Michet CJ, Crowson CS, O'Fallon WM, Gabriel SE. Epidemiology of gout: is the incidence rising? J Rheumatol. 2002;29:2403–2406. - PubMed
-
- Lawrence RC, Felson DT, Helmick CG, Arnold LM, Choi H, Deyo RA, Gabriel S, Hirsch R, Hochberg MC, Hunder GG, Jordan JM, Katz JN, Kremers HM, Wolfe F. Estimates of the prevalence of arthritis and other rheumatic conditions in the United States. Part II. Arthritis Rheum. 2008;58:26–35. doi: 10.1002/art.23176. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Wallace KL, Riedel AA, Joseph-Ridge N, Wortmann R. Increasing prevalence of gout and hyperuricemia over 10 years among older adults in a managed care population. J Rheumatol. 2004;31:1582–1587. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

