Robotics versus laparoscopy--an experimental study of the transfer effect in maiden users
- PMID: 20370924
- PMCID: PMC2857839
- DOI: 10.1186/1750-1164-4-3
Robotics versus laparoscopy--an experimental study of the transfer effect in maiden users
Abstract
Background: Robot-assisted laparoscopy (RL) is used in a wide range of operative interventions, but the advantage of this technique over conventional laparoscopy (CL) remains unclear. Studies comparing RL and CL are scarce. The present study was performed to test the hypothesis that maiden users master surgical tasks quicker with the robot-assisted laparoscopy technique than with the conventional laparoscopy technique.
Methods: 20 subjects, with no prior surgical experience, performed three different surgical tasks in a standardized experimental setting, repeated four times with each of the RL and CL techniques. Speed and accuracy were measured. A cross-over technique was used to eliminate gender bias and the experience gained by carrying out the first part of the study.
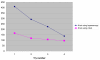
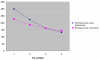
Results: The task "tie a knot" was performed faster with the RL technique than with CL. Furthermore, shorter operating times were observed when changing from CL to RL. There were no time differences for the tasks of grabbing the needle and continuous suturing between the two operating techniques. Gender did not influence the results.
Conclusion: The more advanced task of tying a knot was performed faster using the RL technique than with CL. Simpler surgical interventions were performed equally fast with either technique. Technical skills acquired during the use of CL were transferred to the RL technique. The lack of tactile feedback in RL seemed to matter. There were no differences between males and females.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Distraction and proficiency in laparoscopy: 2D versus robotic console 3D immersion.Surg Endosc. 2017 Nov;31(11):4625-4630. doi: 10.1007/s00464-017-5525-x. Epub 2017 Apr 13. Surg Endosc. 2017. PMID: 28409364 Clinical Trial.
-
Robot assisted versus laparoscopic suturing learning curve in a simulated setting.Surg Endosc. 2020 Aug;34(8):3679-3689. doi: 10.1007/s00464-019-07263-2. Epub 2019 Nov 21. Surg Endosc. 2020. PMID: 31754849 Free PMC article.
-
Severe perioperative morbidity after robot-assisted versus conventional laparoscopy in gynecologic oncology: Results of the randomized ROBOGYN-1004 trial.Gynecol Oncol. 2020 Aug;158(2):382-389. doi: 10.1016/j.ygyno.2020.05.010. Epub 2020 May 25. Gynecol Oncol. 2020. PMID: 32467054 Clinical Trial.
-
What's the best minimal invasive approach to pediatric nephrectomy and heminephrectomy: conventional laparoscopy (CL), single-site (LESS) or robotics (RAS)?Transl Pediatr. 2016 Oct;5(4):240-244. doi: 10.21037/tp.2016.09.01. Transl Pediatr. 2016. PMID: 27867846 Free PMC article. Review.
-
[Laparoscopic knot tying].Magy Seb. 2008 Jun;61(3):116-20. doi: 10.1556/MaSeb.61.2008.3.2. Magy Seb. 2008. PMID: 18515215 Review. Hungarian.
Cited by
-
Visuospatial abilities and fine motor experiences influence acquisition and maintenance of fundamentals of laparoscopic surgery (FLS) task performance.Surg Endosc. 2018 Nov;32(11):4639-4648. doi: 10.1007/s00464-018-6220-2. Epub 2018 May 18. Surg Endosc. 2018. PMID: 29777356
-
Ten years of paediatric robotic surgery: Lessons learned.Int J Med Robot. 2022 Aug;18(4):e2386. doi: 10.1002/rcs.2386. Epub 2022 Mar 11. Int J Med Robot. 2022. PMID: 35240727 Free PMC article.
-
Robotic technology results in faster and more robust surgical skill acquisition than traditional laparoscopy.J Robot Surg. 2015 Mar;9(1):67-73. doi: 10.1007/s11701-014-0493-9. Epub 2014 Dec 24. J Robot Surg. 2015. PMID: 26530974
-
Robotic assistance helps low-volume surgeons deliver better outcomes to their patients.Indian J Urol. 2021 Jan-Mar;37(1):1-3. doi: 10.4103/iju.IJU_216_20. Indian J Urol. 2021. PMID: 33850347 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
European Association of Endoscopic Surgeons (EAES) consensus statement on the use of robotics in general surgery.Surg Endosc. 2015 Feb;29(2):253-88. doi: 10.1007/s00464-014-3916-9. Epub 2014 Nov 8. Surg Endosc. 2015. PMID: 25380708
References
-
- Heemskerk J, van Gemert WG, de Vries J, Greve JW, Bouvy ND. Learning curves of Robot-assisted Laparoscopic Surgery Compared With Conventional Laparoscopic Surgery: An Experimental Study Evaluating Skill Acquisition of Robot-assisted Laparoscopic Tasks Compared With Conventional Laparoscopic Tasks in Inexperienced Users. Surg Laparosc Endosc Percutan Tech. 2007;17:171–174. doi: 10.1097/SLE.0b013e31805b8346. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Olthof E, Nio D, Bemelman WA. In: Medical robotics. Bozovic V, editor. Vienna: I-Tech Education and Publishing; 2008. The learning curve of robot-assisted laparoscopic surgery; pp. 1–8.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

