Assignment of chromosomal locations for unassigned SNPs/scaffolds based on pair-wise linkage disequilibrium estimates
- PMID: 20370931
- PMCID: PMC2859757
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2105-11-171
Assignment of chromosomal locations for unassigned SNPs/scaffolds based on pair-wise linkage disequilibrium estimates
Abstract
Background: Recent developments of high-density SNP chips across a number of species require accurate genetic maps. Despite rapid advances in genome sequence assembly and availability of a number of tools for creating genetic maps, the exact genome location for a number of SNPs from these SNP chips still remains unknown. We have developed a locus ordering procedure based on linkage disequilibrium (LODE) which provides estimation of the chromosomal positions of unaligned SNPs and scaffolds. It also provides an alternative means for verification of genetic maps. We exemplified LODE in cattle.
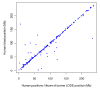
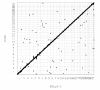
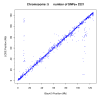
Results: The utility of the LODE procedure was demonstrated using data from 1,943 bulls genotyped for 73,569 SNPs across three different SNP chips. First, the utility of the procedure was tested by analysing the masked positions of 1,500 randomly-chosen SNPs with known locations (50 from each chromosome), representing three classes of minor allele frequencies (MAF), namely >0.05, 0.01<MAF < or = 0.05 and 0.001<MAF < or = 0.01. The efficiency (percentage of masked SNPs that could be assigned a location) was 96.7%, 30.6% and 2.0%; with an accuracy (the percentage of SNPs assigned correctly) of 99.9%, 98.9% and 33.3% in the three classes of MAF, respectively. The average precision for placement of the SNPs was 914, 3,137 and 6,853 kb, respectively. Secondly, 4,688 of 5,314 SNPs unpositioned in the Btau4.0 assembly were positioned using the LODE procedure. Based on these results, the positions of 485 unordered scaffolds were determined. The procedure was also used to validate the genome positions of 53,068 SNPs placed on Btau4.0 bovine assembly, resulting in identification of problem areas in the assembly. Finally, the accuracy of the LODE procedure was independently validated by comparative mapping on the hg18 human assembly.
Conclusion: The LODE procedure described in this study is an efficient and accurate method for positioning SNPs (MAF>0.05), for validating and checking the quality of a genome assembly, and offers a means for positioning of unordered scaffolds containing SNPs. The LODE procedure will be helpful in refining genome sequence assemblies, especially those being created from next-generation sequencing where high-throughput SNP discovery and genotyping platforms are integrated components of genome analysis.
Figures
Similar articles
-
A linkage disequilibrium-based approach to position unmapped SNPs in crop species.BMC Genomics. 2021 Oct 29;22(1):773. doi: 10.1186/s12864-021-08116-w. BMC Genomics. 2021. PMID: 34715779 Free PMC article.
-
The development and characterization of a 60K SNP chip for chicken.BMC Genomics. 2011 May 31;12(1):274. doi: 10.1186/1471-2164-12-274. BMC Genomics. 2011. PMID: 21627800 Free PMC article.
-
Application of massive parallel sequencing to whole genome SNP discovery in the porcine genome.BMC Genomics. 2009 Aug 12;10:374. doi: 10.1186/1471-2164-10-374. BMC Genomics. 2009. PMID: 19674453 Free PMC article.
-
Linkage disequilibrium maps and disease-association mapping.Methods Mol Biol. 2007;376:109-21. doi: 10.1007/978-1-59745-389-9_8. Methods Mol Biol. 2007. PMID: 17984541 Review.
-
The extent of linkage disequilibrium and computational challenges of single nucleotide polymorphisms in genome-wide association studies.Curr Drug Metab. 2011 Jun;12(5):498-506. doi: 10.2174/138920011795495312. Curr Drug Metab. 2011. PMID: 21453276 Review.
Cited by
-
Revealing misassembled segments in the bovine reference genome by high resolution linkage disequilibrium scan.BMC Genomics. 2016 Sep 5;17(1):705. doi: 10.1186/s12864-016-3049-8. BMC Genomics. 2016. PMID: 27595709 Free PMC article.
-
Age- and disease-dependent HERV-W envelope allelic variation in brain: association with neuroimmune gene expression.PLoS One. 2011 Apr 29;6(4):e19176. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0019176. PLoS One. 2011. PMID: 21559469 Free PMC article.
-
SNPrune: an efficient algorithm to prune large SNP array and sequence datasets based on high linkage disequilibrium.Genet Sel Evol. 2018 Jun 26;50(1):34. doi: 10.1186/s12711-018-0404-z. Genet Sel Evol. 2018. PMID: 29940846 Free PMC article.
-
LDscaff: LD-based scaffolding of de novo genome assemblies.BMC Bioinformatics. 2020 Dec 28;21(Suppl 21):570. doi: 10.1186/s12859-020-03895-7. BMC Bioinformatics. 2020. PMID: 33371875 Free PMC article.
-
A linkage disequilibrium-based approach to position unmapped SNPs in crop species.BMC Genomics. 2021 Oct 29;22(1):773. doi: 10.1186/s12864-021-08116-w. BMC Genomics. 2021. PMID: 34715779 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ramos AM, Crooijmans RP, Affara NA, Amaral AJ, Archibald AL, Beever JE, Bendixen C, Churcher C, Clark R, Dehais P. Design of a high density SNP genotyping assay in the pig using SNPs identified and characterized by next generation sequencing technology. PLoS ONE. 2009;4(8):e6524. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0006524. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

