Effects of metabotropic glutamate receptor 2/3 agonism and antagonism on schizophrenia-like cognitive deficits induced by phencyclidine in rats
- PMID: 20371228
- PMCID: PMC2891116
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2009.12.040
Effects of metabotropic glutamate receptor 2/3 agonism and antagonism on schizophrenia-like cognitive deficits induced by phencyclidine in rats
Abstract
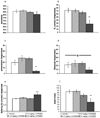
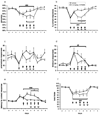
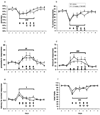
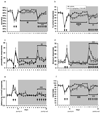
Dysregulation of glutamate neurotransmission may play a role in cognitive deficits in schizophrenia. Manipulation of glutamate signaling using drugs acting at metabotropic glutamate receptors has been suggested as a novel approach to treating schizophrenia-related cognitive dysfunction. We examined how the metabotropic glutamate receptor 2/3 agonist LY379268 and the metabotropic glutamate receptor 2/3 antagonist LY341495 altered phencyclidine-induced disruptions in performance in the 5-choice serial reaction time task. This test assesses multiple cognitive modalities characteristically impaired in schizophrenia that are disrupted by phencyclidine administration. Acute LY379268 alone did not affect 5-choice serial reaction time task performance, except for nonspecific response suppression at high doses. Acute LY379268 administration exacerbated phencyclidine-induced disruption of attentional performance in this task, while acute LY341495 did not alter 5-choice serial reaction time task performance during phencyclidine exposure. Chronic LY341495 impaired attentional performance in the 5-choice serial reaction time task by itself, but attenuated phencyclidine-induced excessive timeout responding. The mixed effects of metabotropic glutamate receptor 2/3 agonism and antagonism on cognitive performance under baseline conditions and after disruption with phencyclidine demonstrate that different aspects of cognition may respond differently to a given pharmacological manipulation, indicating that potential antipsychotic or pro-cognitive medications need to be tested for their effects on a range of cognitive modalities. Our findings also suggest that additional mechanisms, besides cortical glutamatergic transmission, may be involved in certain cognitive dysfunctions in schizophrenia.
Copyright (c) 2010 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Figures

References
-
- Abekawa T, Honda M, Ito K, Koyama T. Effects of NRA0045, a novel potent antagonist at dopamine D4, 5-HT2A, and α1 adrenaline receptors, and NRA0160, a selective D4 receptor antagonist, on phencyclidine-induced behavior and glutamate release in rats. Psychopharmacology (Berl.) 2003;169:247–256. - PubMed
-
- Adams BW, Moghaddam B. Effect of clozapine, haloperidol, or M100907 on phencyclidine-activated glutamate efflux in the prefrontal cortex. Biol. Psychiatry. 2001;50:750–757. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

