Cognitive effects of Group I metabotropic glutamate receptor ligands in the context of drug addiction
- PMID: 20371237
- PMCID: PMC2891107
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2010.01.029
Cognitive effects of Group I metabotropic glutamate receptor ligands in the context of drug addiction
Abstract
Glutamate plays a pivotal role in regulating drug self-administration and drug-seeking behavior, and the past decade has witnessed a substantial surge of interest in the role of Group I metabotropic glutamate receptors (mGlu(1) and mGlu(5) receptors) in mediating these behaviors. As will be reviewed here, Group I mGlu receptors are involved in normal and drug-induced synaptic plasticity, drug reward, reinforcement and relapse-like behaviors, and addiction-related cognitive processes such as maladaptive learning and memory, behavioral inflexibility, and extinction learning. Animal models of addiction have revealed that antagonists of Group I mGlu receptors, particularly the mGlu(5) receptor, reduce self-administration of virtually all drugs of abuse. Since inhibitors of mGlu5 receptor function have now entered clinical trials for other medical conditions and appear to be well-tolerated, a key question that remains unanswered is - what changes in cognition are produced by these compounds that result in reduced drug intake and drug-seeking behavior? Finally, in contrast to mGlu(5) receptor antagonists, recent studies have indicated that positive allosteric modulation of mGlu(5) receptors actually enhances synaptic plasticity and improves various aspects of cognition, including spatial learning, behavioral flexibility, and extinction of drug-seeking behavior. Thus, while inhibition of Group I mGlu receptor function may reduce drug reward, reinforcement, and relapse-related behaviors, positive allosteric modulation of the mGlu5 receptor subtype may actually enhance cognition and potentially reverse some of the cognitive deficits associated with chronic drug use.
Copyright (c) 2010 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Figures
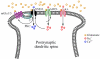
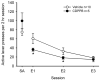
References
-
- Alagarsamy S, Marino MJ, Rouse ST, Gereau R.W.t., Heinemann SF, Conn PJ. Activation of NMDA receptors reverses desensitization of mGluR5 in native and recombinant systems. Nat. Neurosci. 1999;2:234–240. - PubMed
-
- Anwyl R. Metabotropic glutamate receptors: electrophysiological properties and role in plasticity. Brain Res. Rev. 1999;29:83–120. - PubMed
-
- Anwyl R. Metabotropic glutamate receptor-dependent long-term potentiation. Neuropharmacology. 2009;56:735–740. - PubMed
-
- American Psychiatry Association . Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders. 4th Edition, Text Revision American Psychiatric Press; Washington DC: 2002.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

